Designing a focused library of compounds is a central part of molecular modeling, whether for virtual screening, SAR studies, or lead optimization. However, creating diverse analogues by hand can become tedious, especially when you’re tweaking only specific fragments.
The SMILES Manager extension in SAMSON offers a feature that streamlines this process: fragment replacement. It’s an efficient way to generate structural analogues by systematically substituting chemical fragments within a molecule using a simple visual interface. Here’s what it can help you achieve – and how to use it effectively.
Why Fragment Replacement?
Imagine you have a promising hit compound, but you’re unsure which functional group variant will best improve solubility or binding affinity. Instead of drawing new molecules one by one, you can replace a designated fragment in your molecule — such as an amide linker — with a library of alternative fragments with just a few clicks.
Getting Started
Start by heading over to the Replace fragments tab in the SMILES Manager. This tab is visually similar to the main SMILES table but tailored for systematic analog generation.
1. Specify Your Initial Molecule
Provide one or more base molecules. You can:
- Import a .smi or .txt file
- Add molecules manually
- Use a selection from an active SAMSON Document
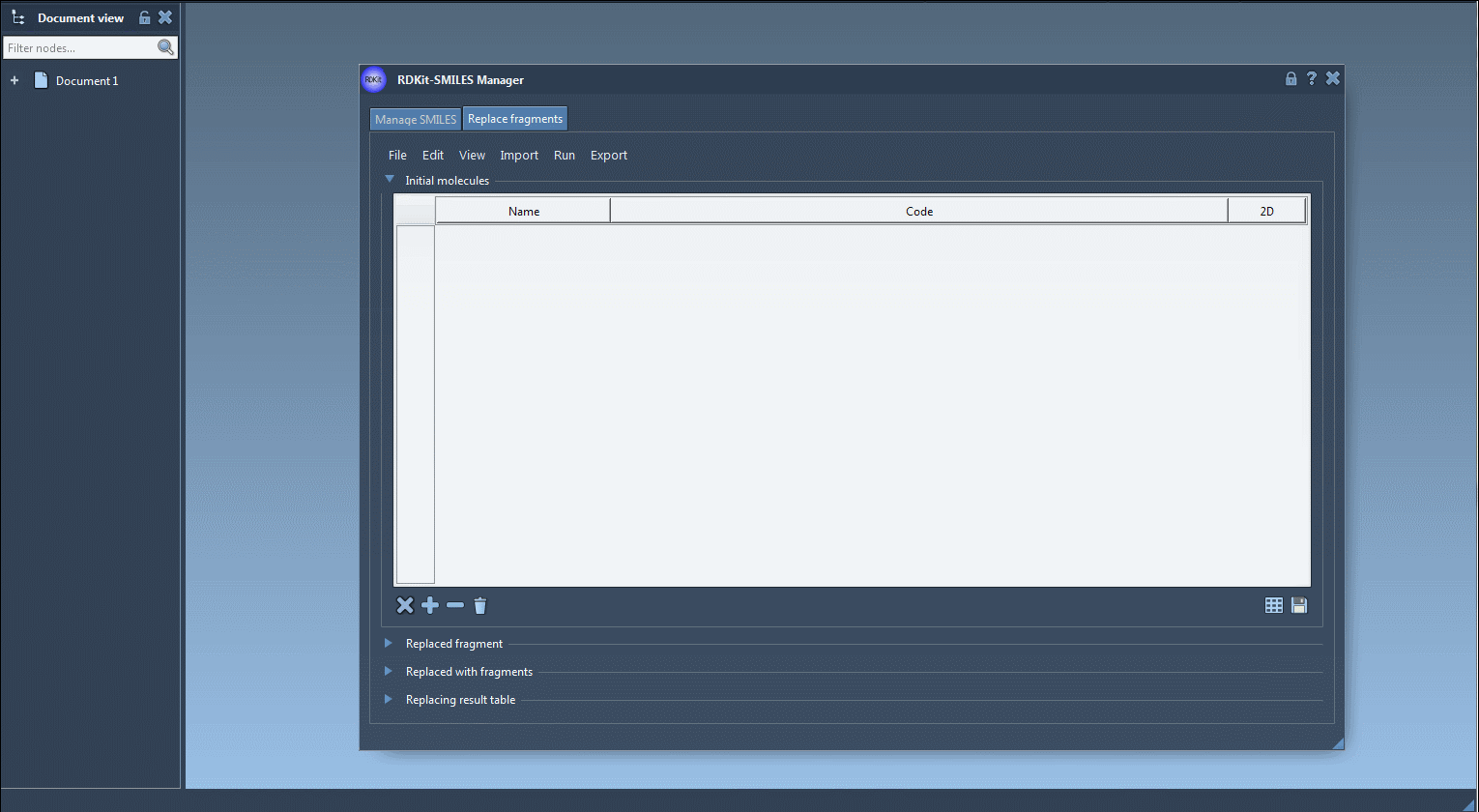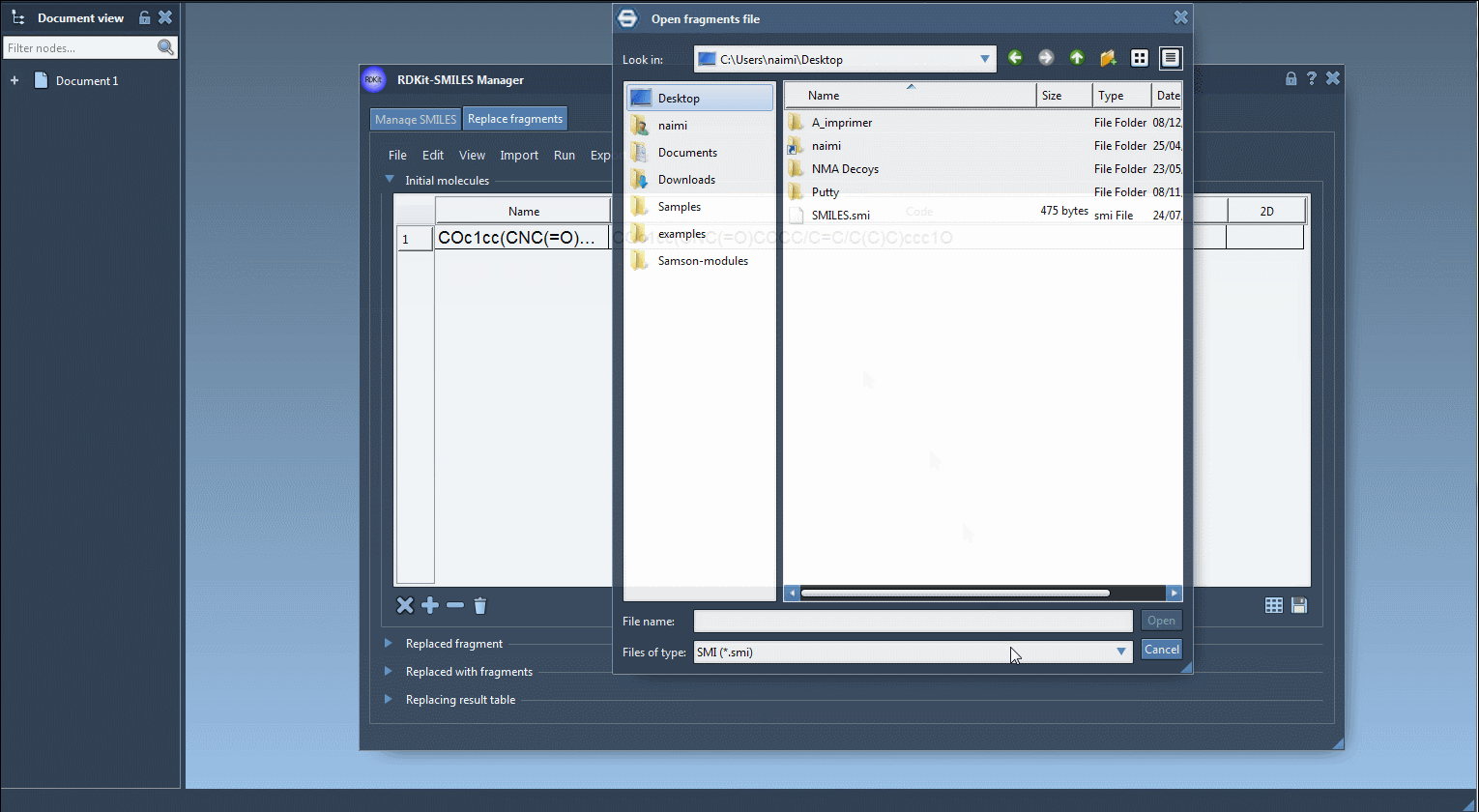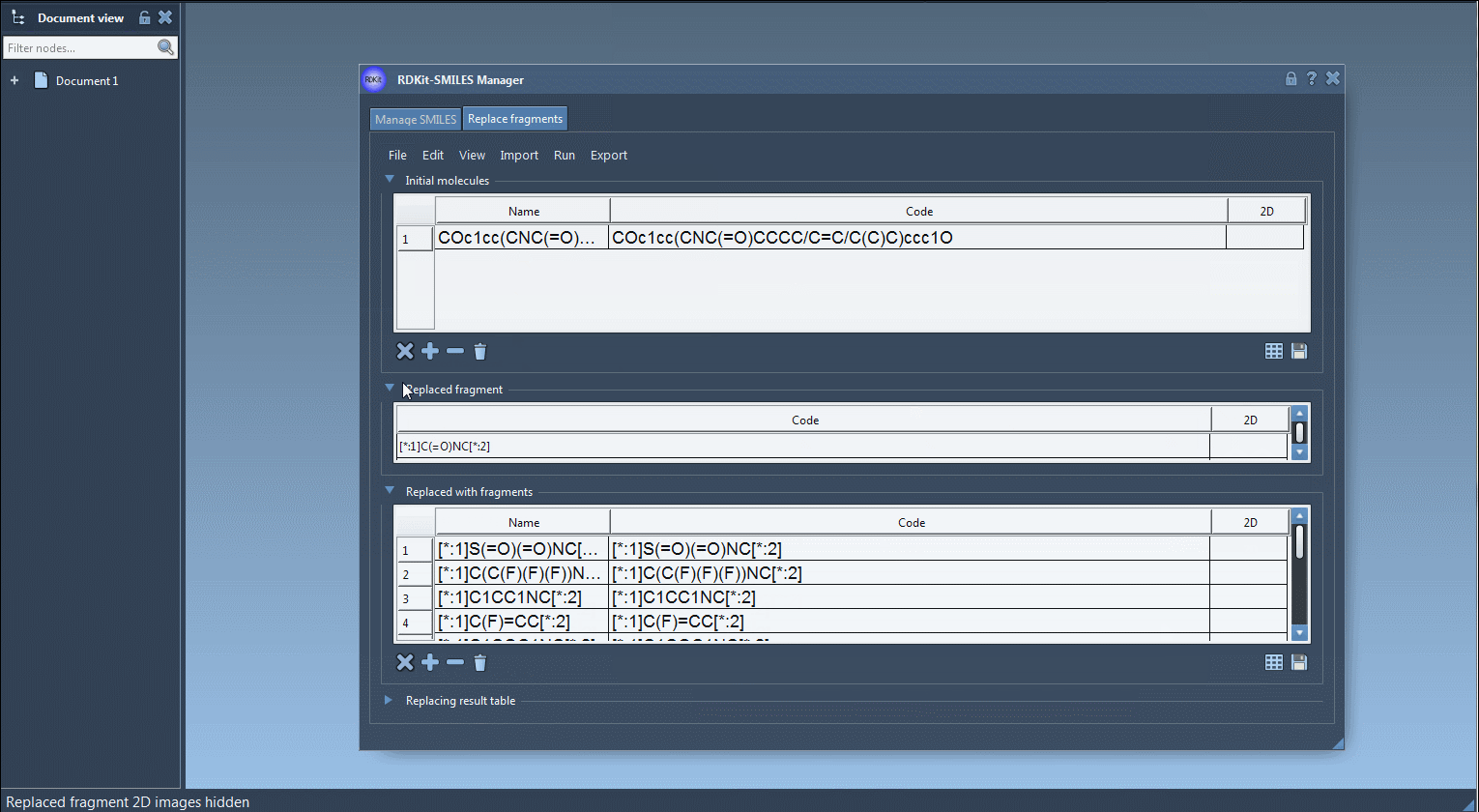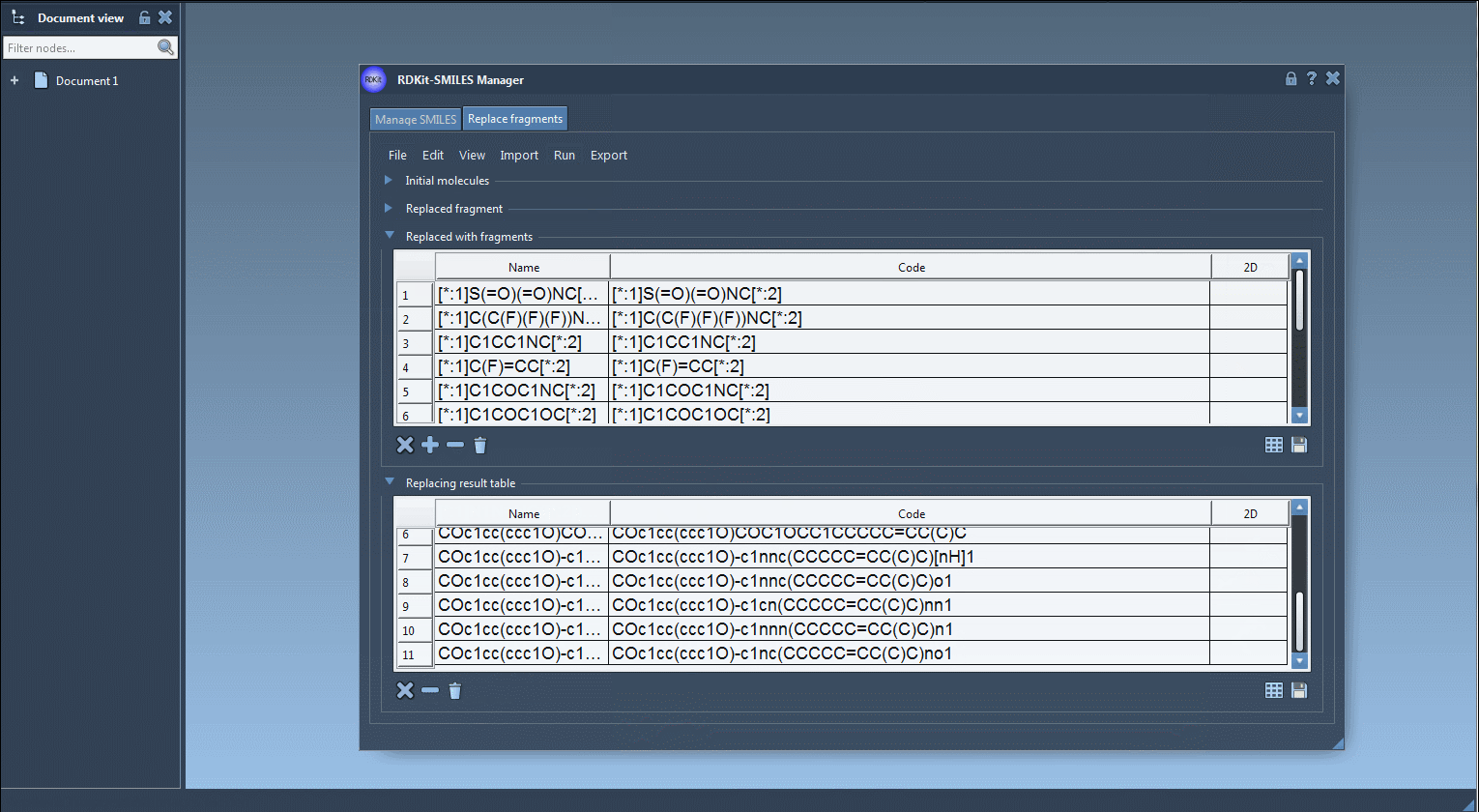
In the tutorial example, we use: COc1cc(CNC(=O)CCCC/C=C/C(C)C)ccc1O
2. Define the Fragment to Replace
Specify which part of your molecule you’re interested in modifying. This is done using SMARTS-like notation. For example:
[*:1]C(=O)NC[*:2]
[*:1] and [*:2] act as placeholders – they mark the connection points for replacement, ensuring proper attachment to the rest of the molecule.
3. Provide Replacement Fragments
You can supply a list of replacement candidates, including from files or by entering them manually. Each must be in the format that uses the same [:*] connection points. Here’s a sample set used in the tutorial:
|
1 2 3 4 |
[*:1]S(=O)(=O)NC[*:2] [*:1]C(C(F)(F)(F))NC[*:2] [*:1]C1CC1NC[*:2] [*:1]C(F)=CC[*:2] |
4. Execute the Replacement
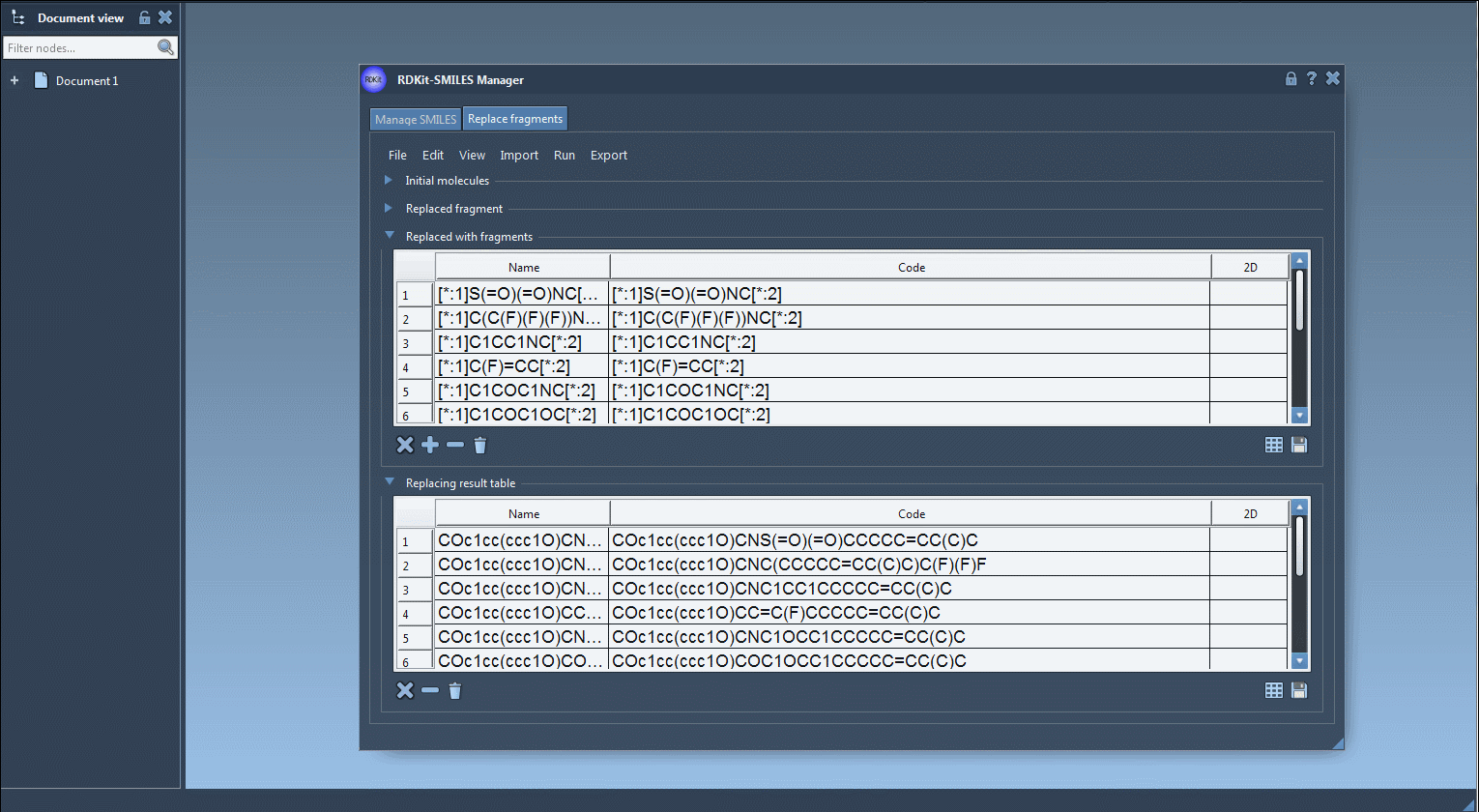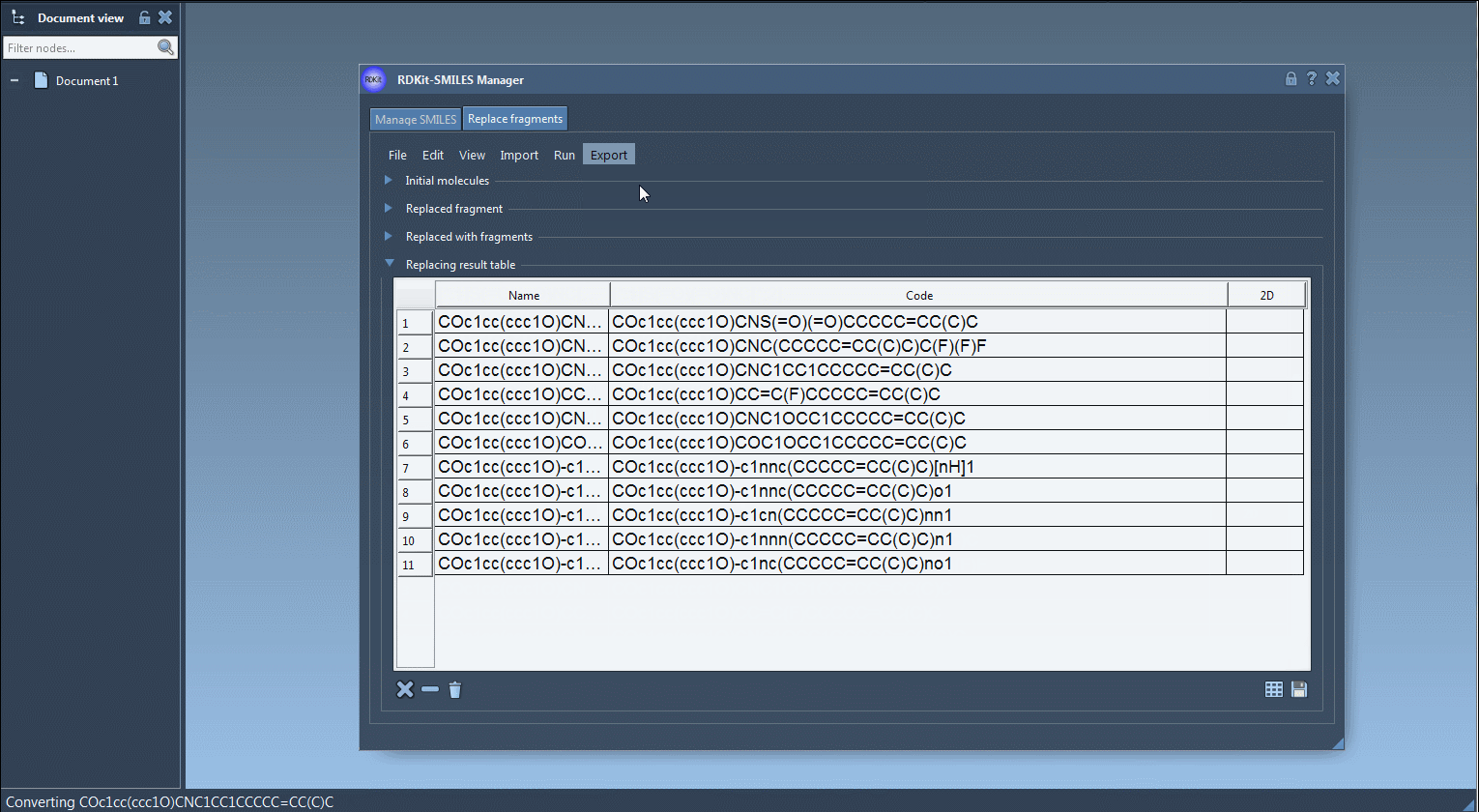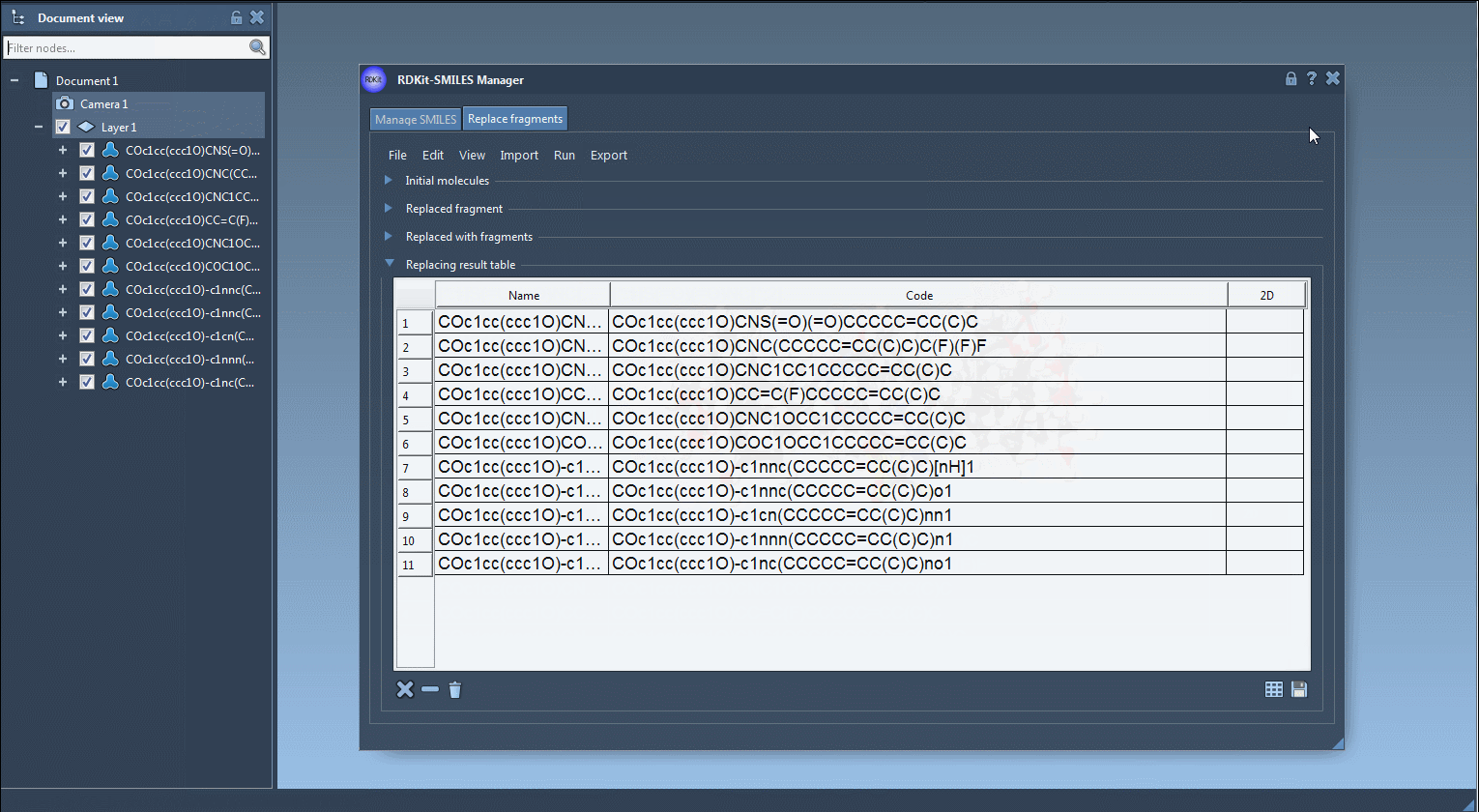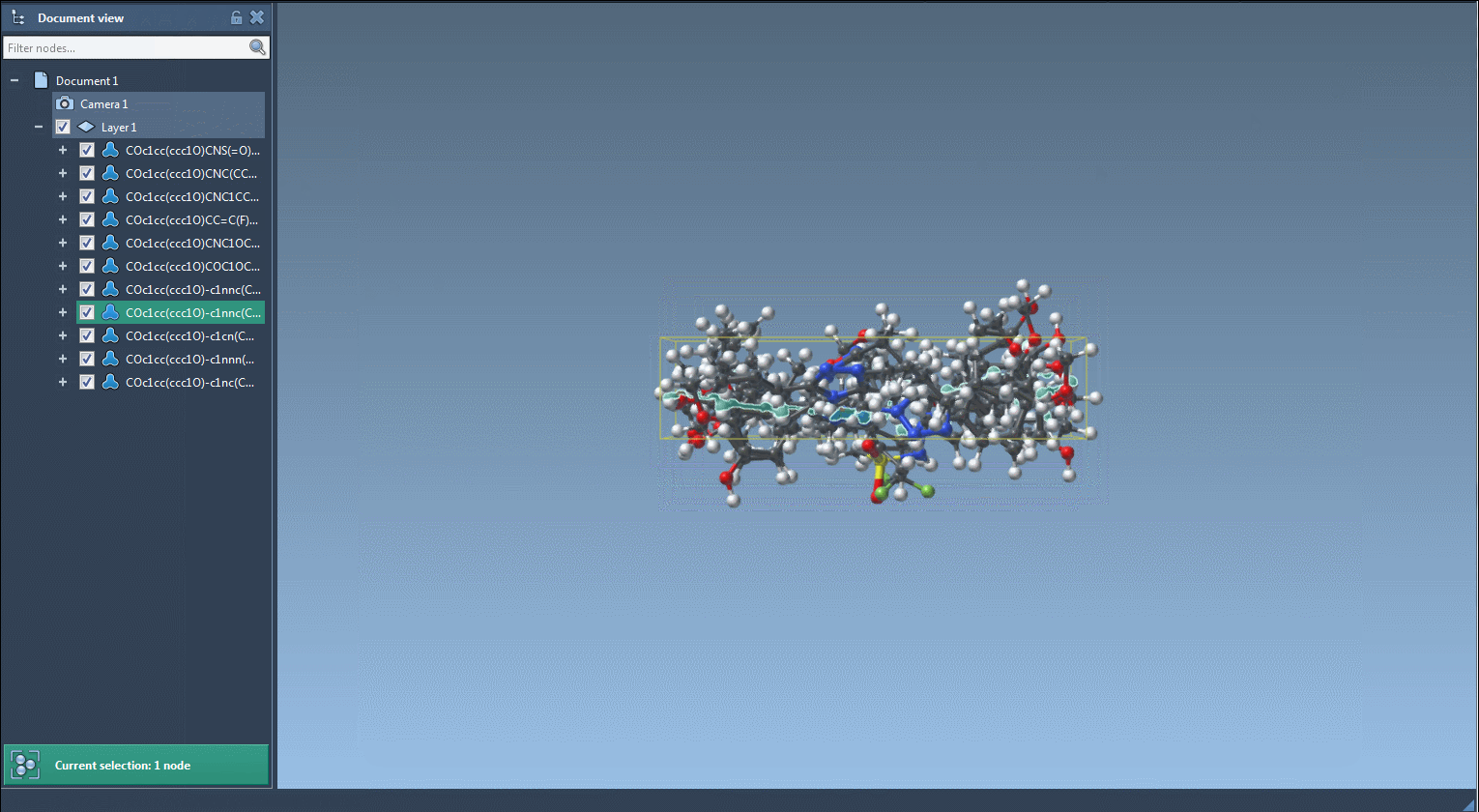
Click “Replace fragments” in the Run menu. SMILES Manager does the heavy lifting and generates a new list of modified molecules.
5. Explore and Export
- Visualize each new molecule in 2D (automatically generated)
- View/export 3D models
- Save molecules to SAMSON documents or image grids
When to Use This
This feature is particularly useful when:
- Exploring isosteric replacements for key substructures
- Creating small virtual libraries around a scaffold
- Studying the impact of linker variants
You can integrate this step into a larger molecular design workflow by exporting results for further modeling, docking, or property prediction.
To learn more, visit the full documentation: Using the SMILES Manager.
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. You can download SAMSON here.





