One common challenge in molecular design is quickly generating diverse analogs of a lead compound to test for biological activity, stability, or solubility—without having to draw every single structure manually. This is especially important in lead optimization phases, where chemists often want to iterate through a variety of isosteric replacements and substitutions.
The SMILES Manager extension in SAMSON provides a meaningful solution to this: an efficient fragment replacement workflow that leverages RDKit under the hood. This functionality lets scientists rapidly generate libraries of new molecules from reference structures by swapping selected substructures with predefined fragments, using SMILES notation and tagged connection points.
How Fragment Replacement Works
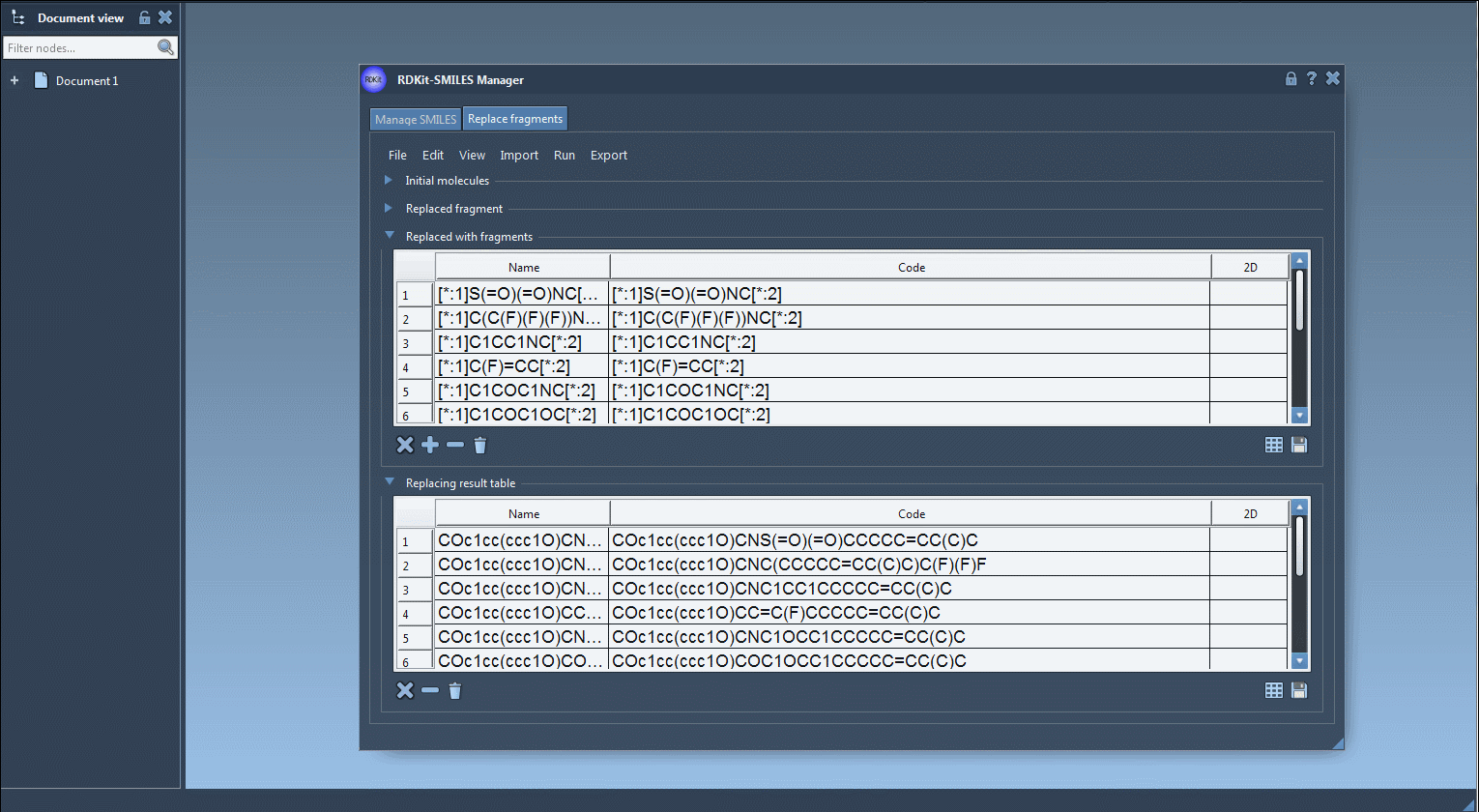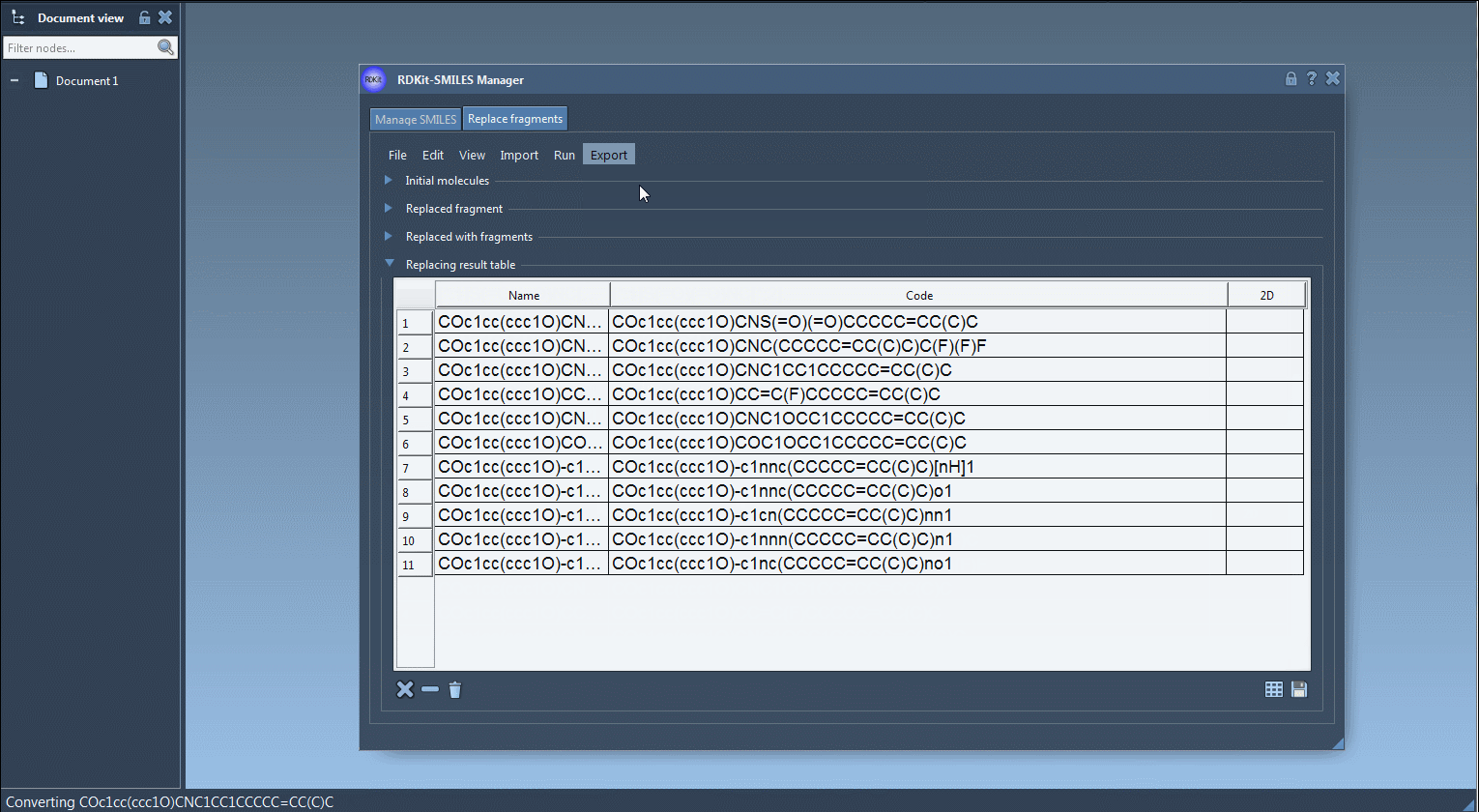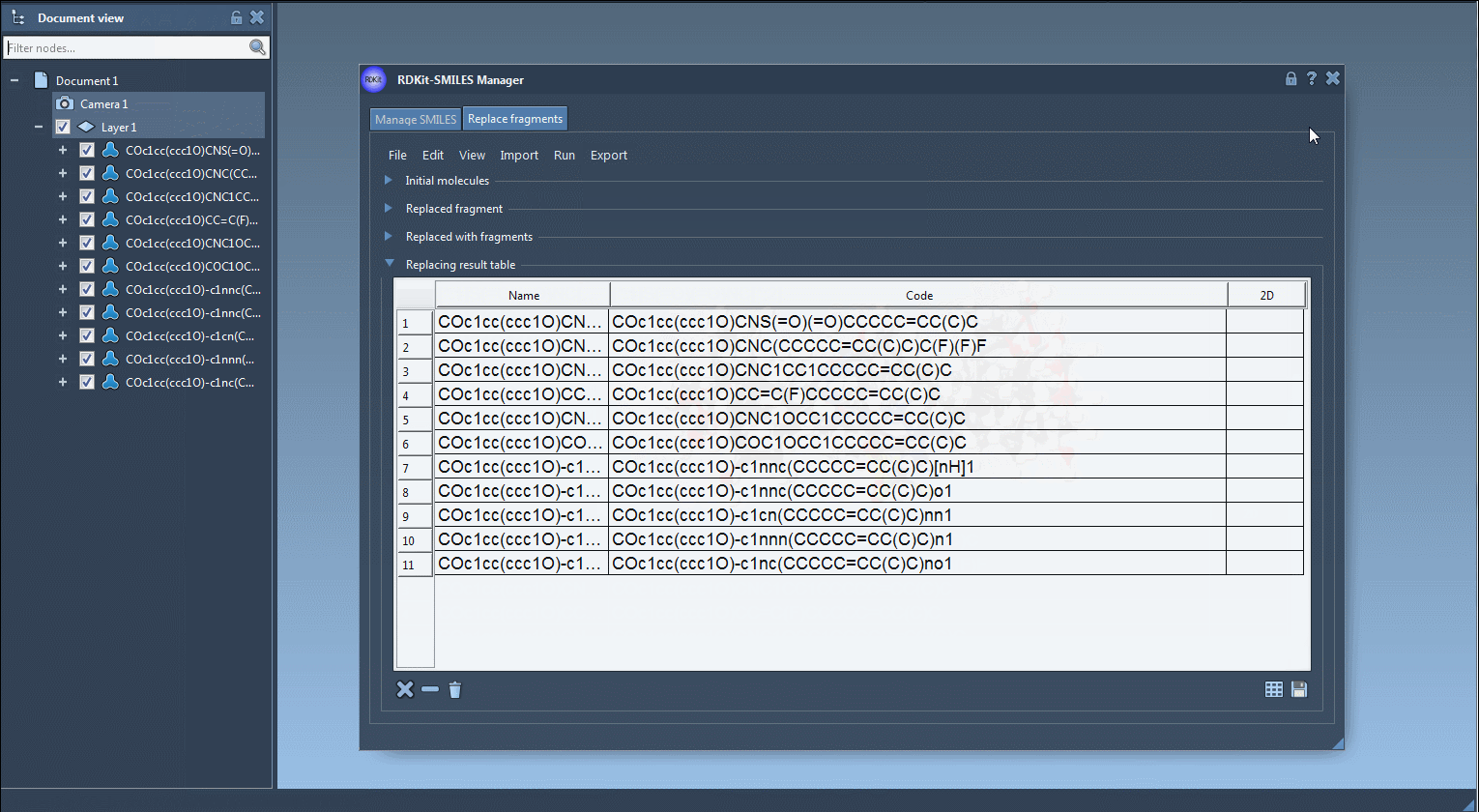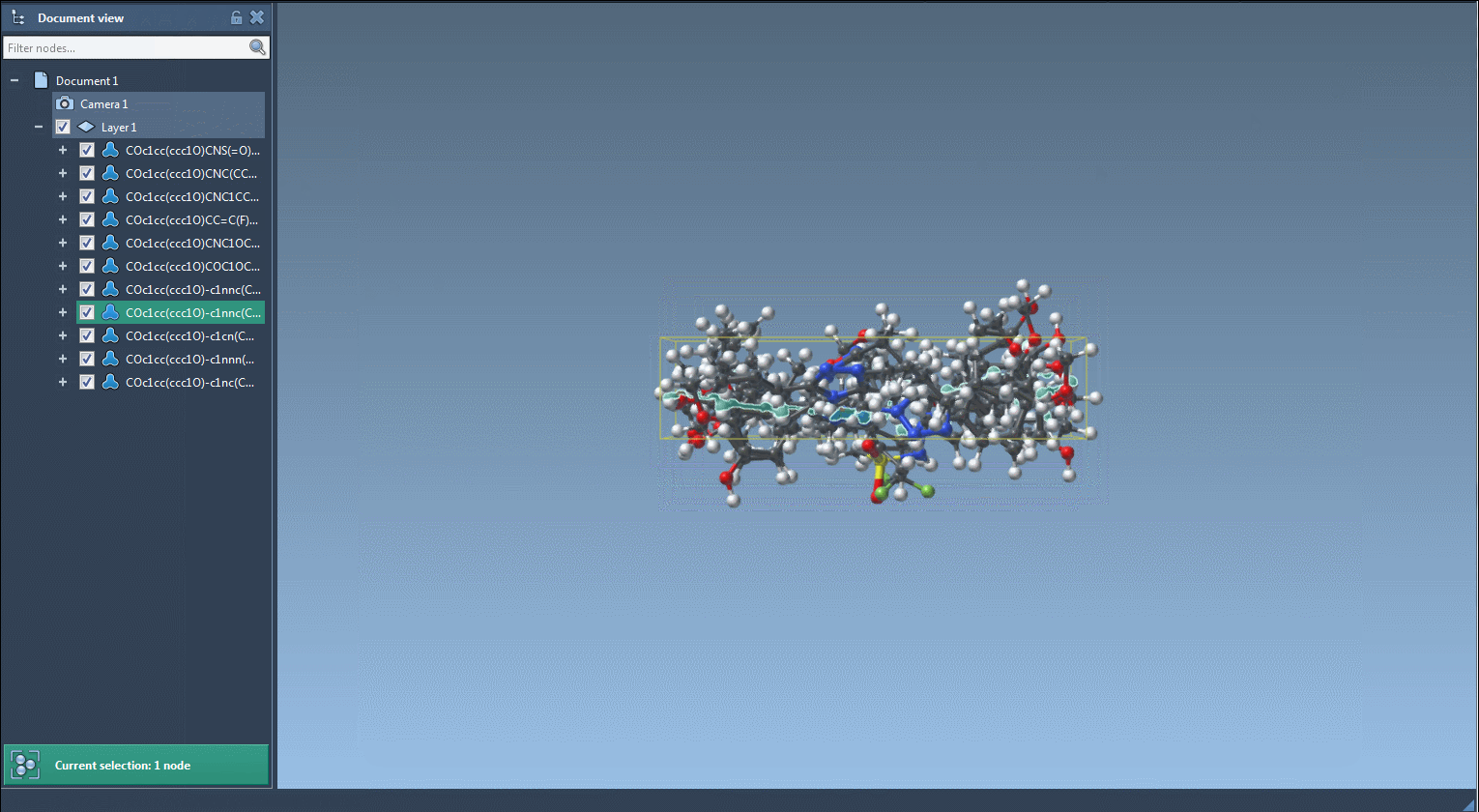
In the Replace fragments tab of the SMILES Manager, users specify three things:
- An initial molecule in SMILES format. For example:
COc1cc(CNC(=O)CCCC/C=C/C(C)C)ccc1O - A fragment to be replaced. This is a SMARTS-like pattern with two connection points, labeled
[*:1]and[*:2]. Example:[*:1]C(=O)NC[*:2] - A list of replacement fragments, all of which must follow RDKit conventions and use the same
[*:1]and[*:2]tags:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
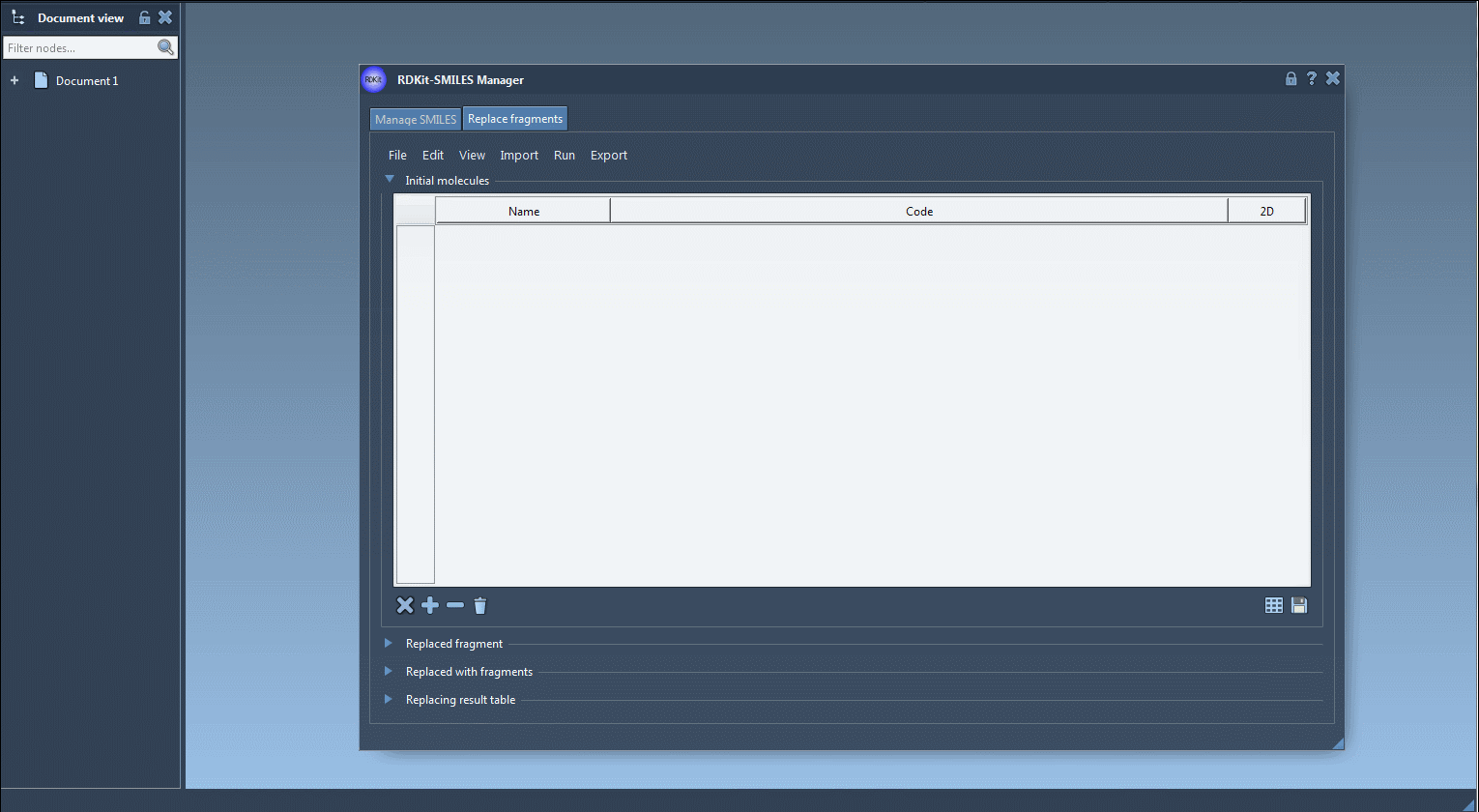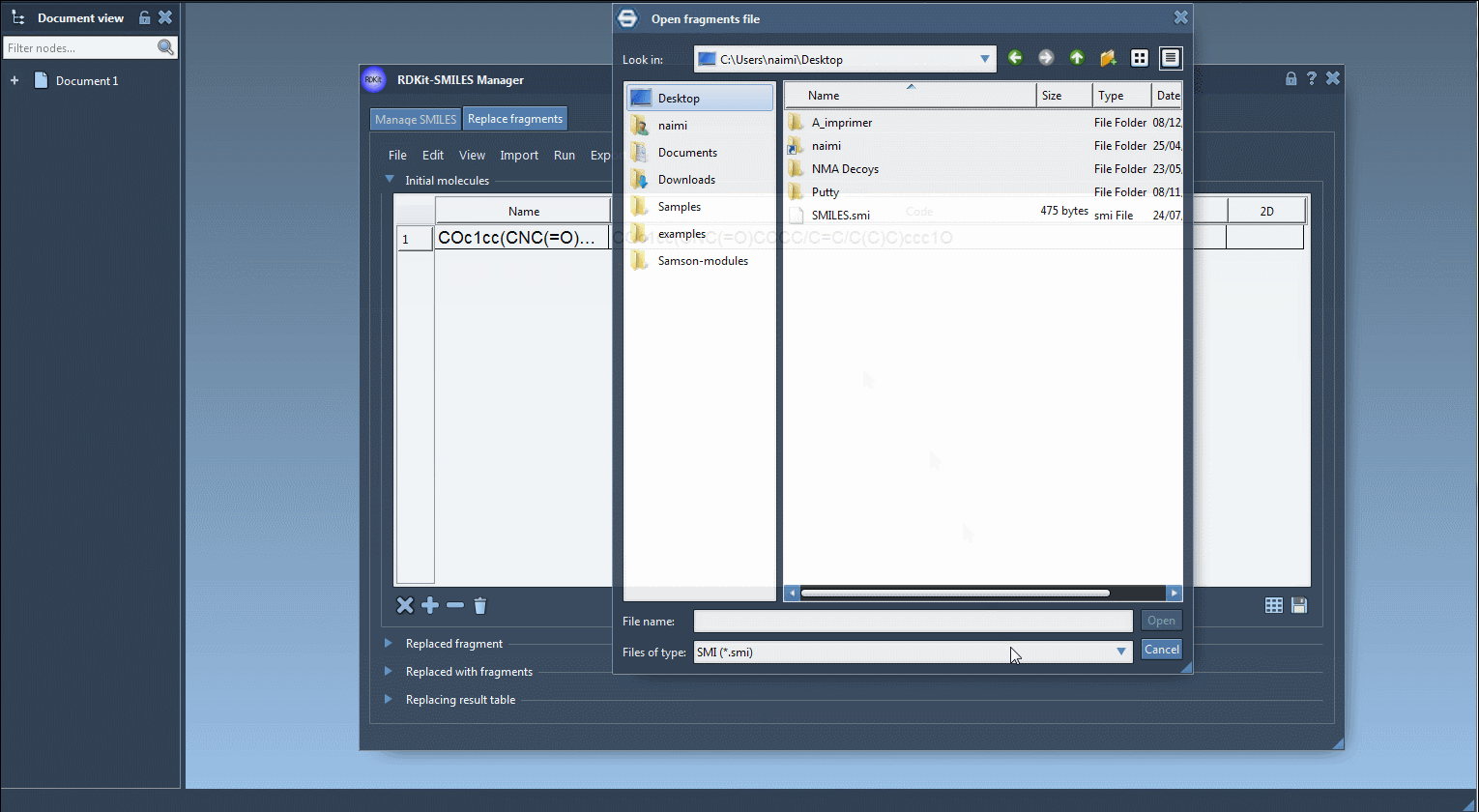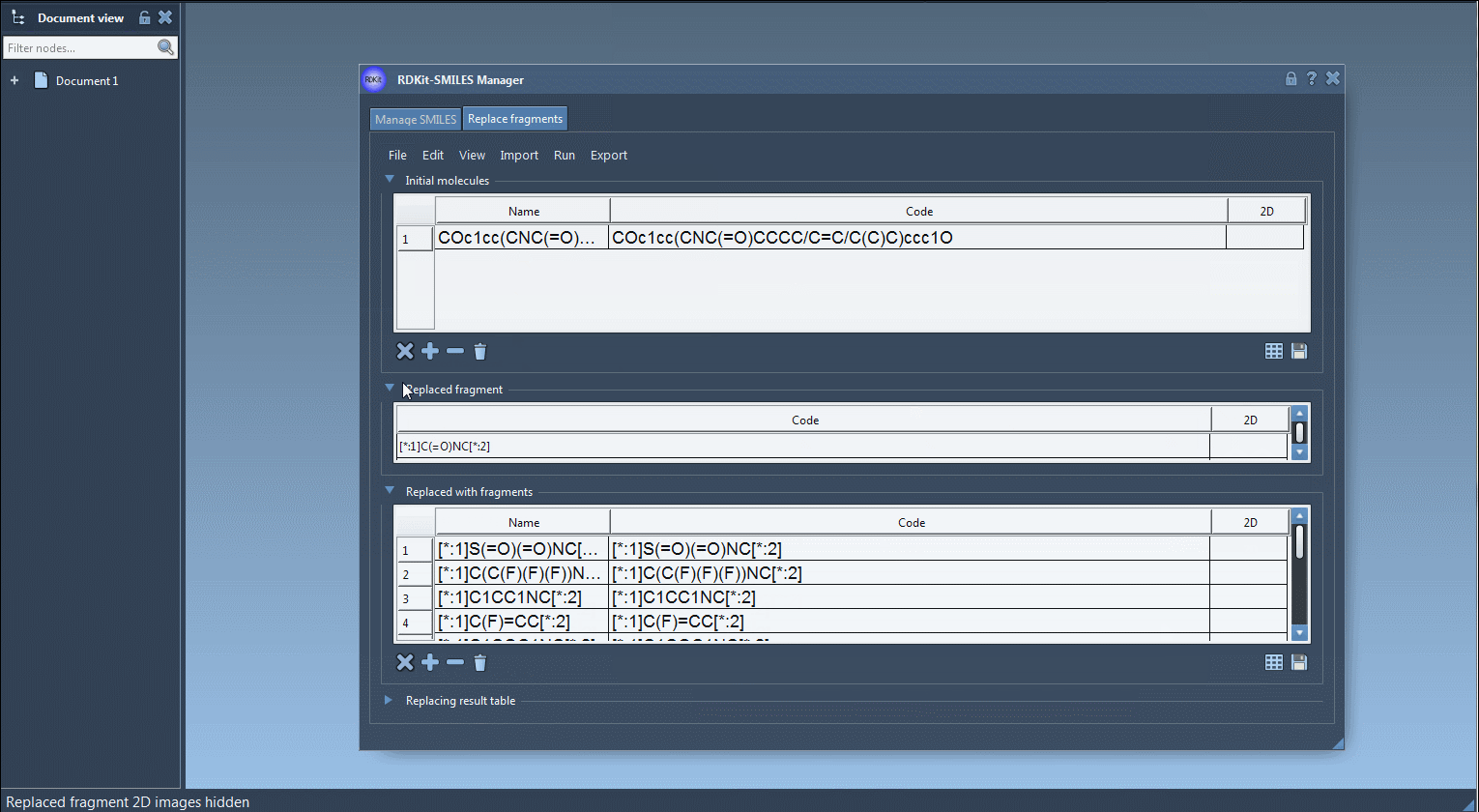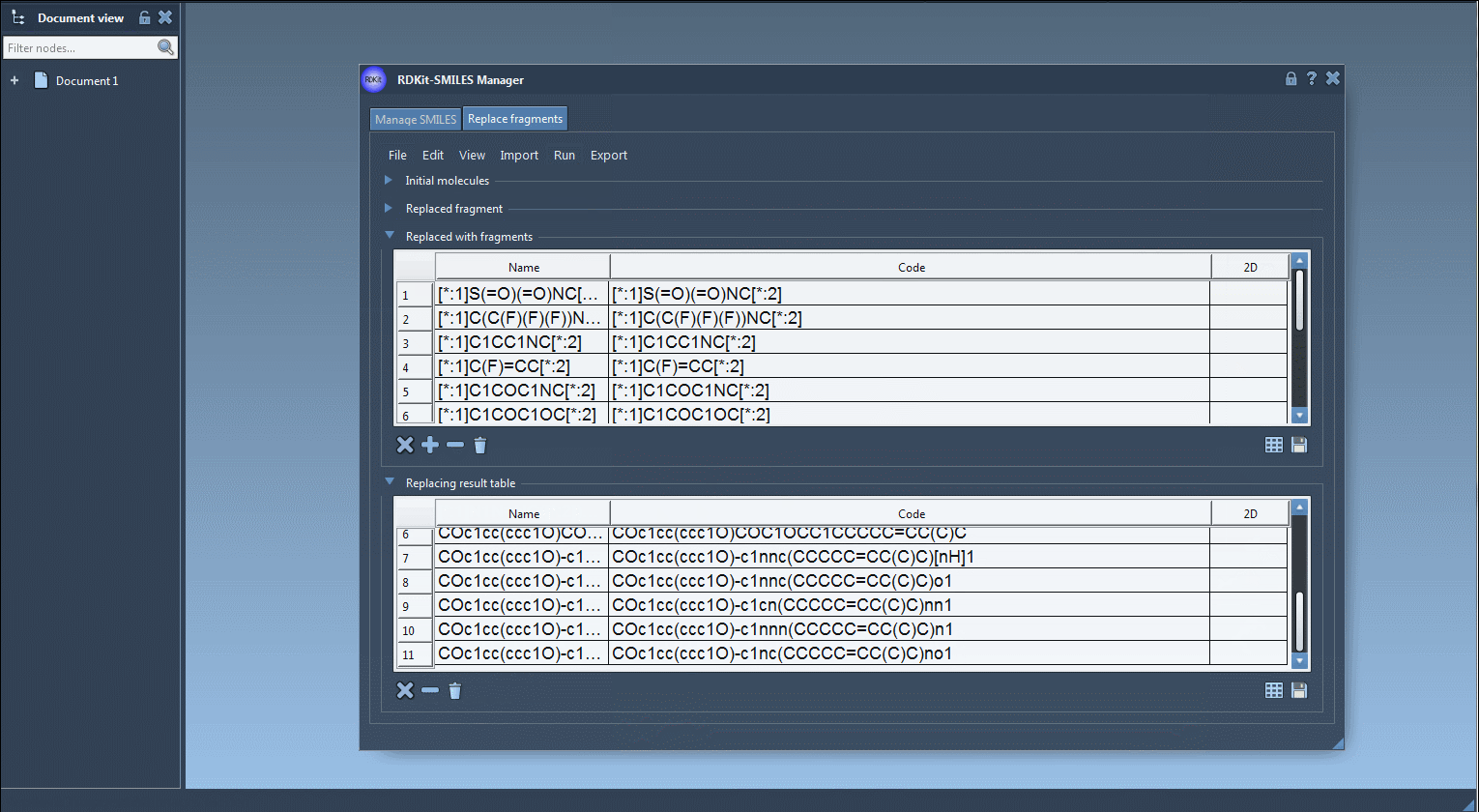
[*:1]S(=O)(=O)NC[*:2] [*:1]C(C(F)(F)(F))NC[*:2] [*:1]C1CC1NC[*:2] [*:1]C(F)=CC[*:2] [*:1]C1COC1NC[*:2] |
Once these inputs are specified, the SMILES Manager generates all output molecules by replacing the target fragment with each candidate from the replacement list. These results are presented in a visual table—each with its name and 2D rendering.
Why It Matters
This kind of automated fragment substitution helps overcome the tediousness of drawing dozens—or hundreds—of analogs. Instead of labor-intensive structure assembly or editing, researchers just work with SMILES strings and modular replacement logic.
Once generated, the resulting structures can be:
- Inspected visually
- Converted to full 3D conformations with a single click
- Exported to files or to the active SAMSON document
- Used in downstream computational workflows (e.g., docking, molecular dynamics)
Quick Tip: SAMSON Integration
The SMILES Manager is fully embedded in SAMSON, meaning that imported molecules, fragments, or results can be manipulated just like any other molecular structure in a SAMSON scene. For example, if you’re using a series of molecules in a project, you can directly select atoms or fragments in the 3D viewer and pass them to the SMILES Manager as input.
Important Conventions
All input fragments must use the RDKit-recommended syntax for atom mapping: connection points must be written like [*:1] and [*:2] to allow proper matching and replacement. Improper labeling may cause failure to generate valid replacements.
Final Thoughts
Fragment replacement with the SMILES Manager provides a practical way for chemists and modelers to generate diverse chemical libraries—they can explore more ideas, faster, and with greater consistency.
To learn more and access detailed tutorials, visit the official SMILES Manager documentation page.
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. You can download SAMSON at samson-connect.net.





