Anyone who regularly models molecular systems knows that managing atom, residue, or structural selections can quickly become a tedious and error-prone task. Whether you’re dealing with large protein complexes, ligands, or custom structural groups, clicking through endless menus or misclicking the wrong atom can lead to wasted time and incorrect simulations.
This is where SAMSON’s Node Specification Language (NSL) becomes extremely useful. With NSL, you can specify exactly what kind of nodes (atoms, residues, bonds, etc.) you want to work with—thanks to a concise, expressive and flexible syntax designed to filter and select molecular components based on their properties or spatial relationships.
Quick and Precise with the Find Command
Instead of manually navigating through a hierarchy, you can use the Find command in the SAMSON interface to input an NSL expression. Pressing the Tab key even provides auto-completions based on the document structure. This is particularly helpful when targeting nodes by name, such as selecting specific residues like alanine ("ALA") or chains:
"ALA 22 Backbone""ALA 28 Side chain"
For example, typing "ALA (with open quote) and pressing Tab brings up all node names starting with ALA. This reduces error and reveals the structure of your model in a context-sensitive way.

Filter Visualizations with Document View
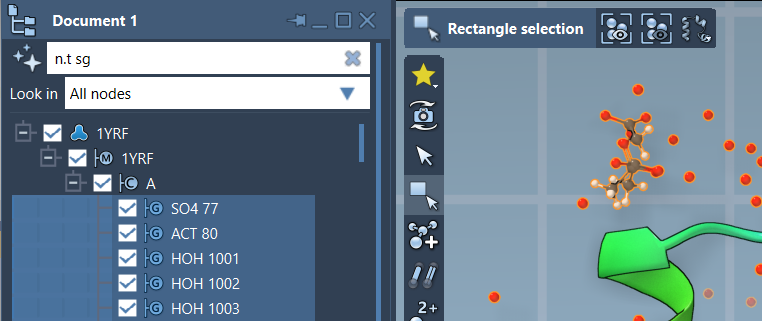
NSL is also integrated directly into the Document View for real-time filtering. Let’s say you want to filter for structural groups. You can use:
n.t sg
to isolate all nodes of type structuralGroup. Press Enter to select them all, or click to focus on individual nodes.
Don’t Guess—Use AI Help
Still unsure about how to write NSL expressions? You don’t have to memorize everything. SAMSON provides an AI Assistant that understands the active document’s structure. You can click on the Ask AI button next to selection fields, and ask natural-language queries such as “show me all non-alanine residues,” and the tool will generate the correct NSL string for you.
Try It Yourself
Here are a few simple NSL expressions to get you started:
node.category ligandorn.c lig— Select ligand nodesH in n.s— Hydrogens in the current selectiona.c A,B,C— Atoms in chains A, B, or Cn.t sc h S— Side chains that have at least one sulfur atom
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, it’s easy to build complex selections using logical (and, not, or), topology (in, having), and proximity operators (within, out of, etc).
To learn more and explore full NSL capabilities, visit the Node Specification Language documentation.
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. You can download the platform at https://www.samson-connect.net.





