Molecular modelers often work with complex structures containing thousands of atoms, residues, ligands, and other node types. Selecting the right subset of these nodes precisely and efficiently can be a challenge, especially during structure analysis, preparing simulations, or performing molecular edits.
Fortunately, in SAMSON, the Node Specification Language (NSL) offers a powerful and flexible way to filter and select nodes — directly within the Document view.
Why Use NSL in the Document View?
The Document view displays structure hierarchies from the current document, allowing users to explore molecules, atoms, bonds, and other elements. Adding NSL capabilities here gives you immediate filtering and selection tools tailored to your data.
Typical pain point:
“I only want to work with specific types of atoms or residues, like side chains, or maybe only structural groups with certain properties. I manually click through the structure tree, but it’s time-consuming and error-prone.”
Enter NSL.
How to Use NSL in the Document View
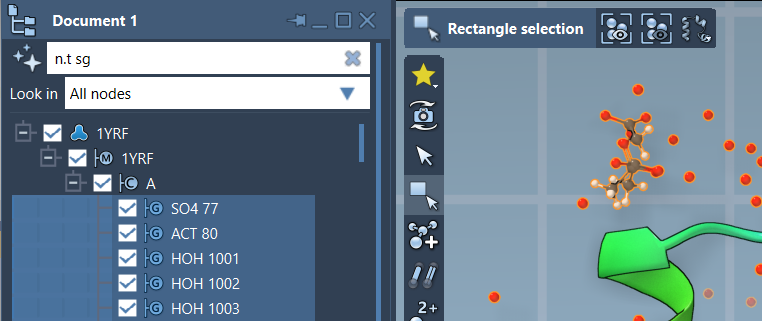
Inside the Document view, there’s a search field where you can type an NSL expression to filter nodes. Once the desired nodes are visible, pressing Enter selects them.
Here’s an example that filters nodes to show only structural groups:
|
1 |
n.t sg |
This is a shorthand for:
|
1 |
node.type structuralGroup |
This filters structural group nodes without selecting others like atoms or chains. After pressing Enter, the filtered nodes become selected in SAMSON.
Even Easier: Ask the AI Assistant
If you’re unsure how to write the NSL expression you need, SAMSON offers an AI Assistant that can generate expressions based on natural language queries. Just click the ![]() button next to the filter box.
button next to the filter box.
This assistant understands the hierarchy of your active document, making it easier to write valid and accurate NSL expressions without needing to remember syntax.
Examples to Try
atom.symbol C— Filter for carbon atoms.r.t ALA— Find all alanine residues.a.charge > 0— Match positively charged atoms.H in r.t ARG— Filter hydrogen atoms in arginine residues.
Want to focus your analysis on ligands or filter based on spatial proximity to a specific group? Use NSL’s proximity and logic operators directly in the Document view to tailor your selections further.
Conclusion
Being able to filter nodes interactively with NSL directly in the Document view helps users simplify complex documents, make well-targeted selections, and save time. It’s especially useful in workflows where selection accuracy is critical.
To learn more about how to build NSL expressions and explore additional examples, visit the Node Specification Language documentation.
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. You can download SAMSON at https://www.samson-connect.net.





