Atom-level editing is central to molecular modeling, yet it’s often tedious to isolate subsets of atoms based on spatial and chemical criteria. Typical visual selection tools can become limiting when working with large structures or when precision is required. If you’ve ever wished for a simpler, faster, or more mathematical way to select atoms inside a structure — especially geometrically — there’s a tool in SAMSON that you might have missed.
This post introduces the Atoms Selector Extension in SAMSON, a powerful utility that allows molecular modelers to select atoms through mathematical expressions. Instead of manually picking atoms or cycling through complex visual filters, you can now just write an expression like you would in a spreadsheet formula or coding environment.
Why Is This Useful?
Imagine you’re preparing a localized modification in a protein, applying restraints in a simulation, or visualizing specific nanostructures. You may want to work only on atoms inside a sphere or cylinder, or perhaps a certain type of atoms above a plane. Picking them one by one is not only slow, but error-prone.
The SAMSON Atoms Selector Extension supports a wide set of atom properties and mathematical expressions to let you do this precisely, reproducibly, and quickly. It leverages the same scripting syntax as the Simple Script Extension, giving you access to coordinates, atomic elements, IDs, charges, and much more.
Use Case: Cutting Cylinders from Crystalline Structures
Here’s a simple but common task: selecting atoms within a cylindrical region — for example, to isolate a nanowire or simulate a functionalized pillar of a material.
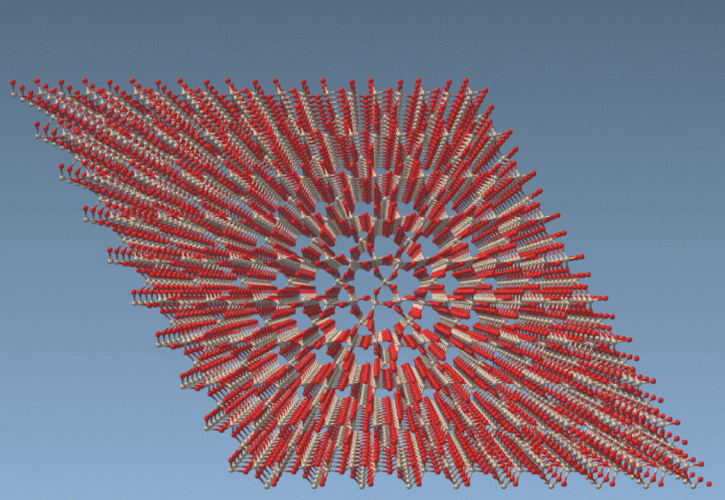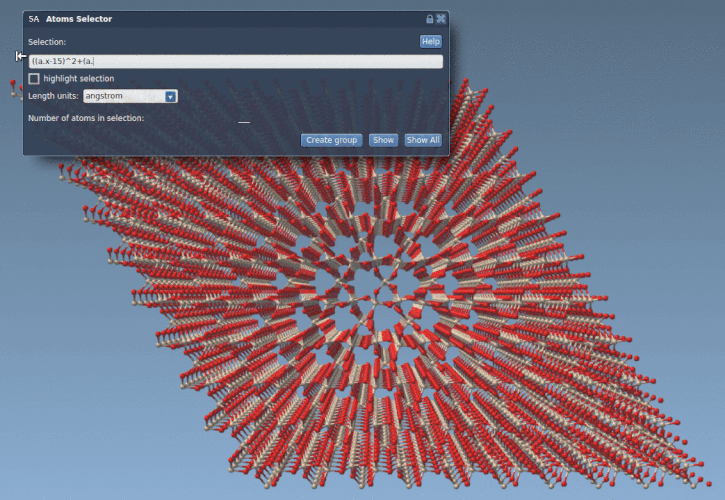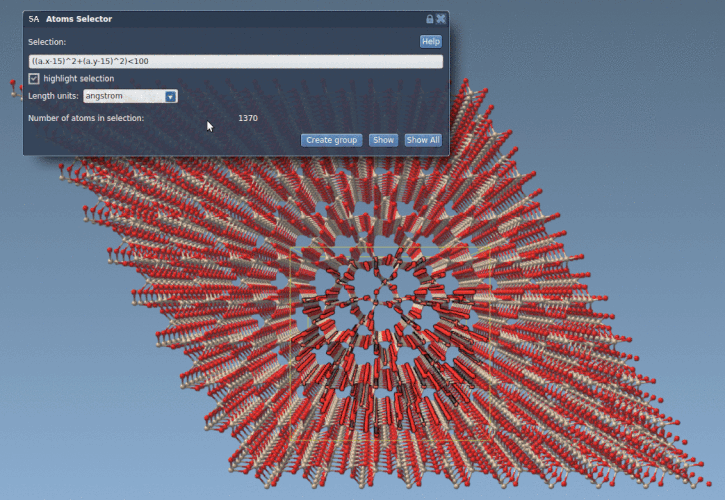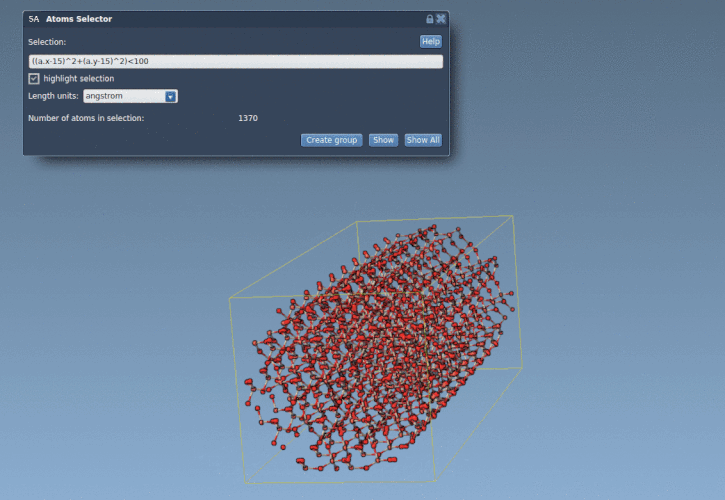
Suppose we have a quartz crystal in your SAMSON workspace and you’d like to extract atoms within 10 Å radius centered at coordinates (15, 15):
|
1 |
((a.x - 15)^2 + (a.y - 15)^2) < 100 |
The above expression uses the positions of atoms and selects only those that lie within the defined circular area in the xy-plane (a cross-section of the cylinder). This is simpler and faster than any manual selection technique.
Key Features
- Use atom position variables:
a.x,a.y,a.z - Use element criteria:
a.symbol=='H',a.element=='Carbon' - Combine logical expressions:
a.x > 0 and a.y < 5 - Support for mathematical functions like
abs(),sin(),log(), etc.
You just write the condition and all atoms satisfying it are automatically selected. There’s also a special keyword all if you want to select everything quickly.
How It Differs from Simple Script
While the Simple Script Extension allows you to change atom properties like position or type, the Atoms Selector focuses purely on selections. This makes it safer and faster when you aren’t modifying structures but just isolating parts of them for analysis or visualization.
Conclusion
Using mathematical expressions for selection introduces flexibility and precision into your modeling workflow. Whether you’re cleaning up a structure, creating substructures, or preparing inputs for simulation, the Atoms Selector Extension provides a precise and reproducible toolkit.
To learn more and explore many more examples, visit the original documentation page: https://documentation.samson-connect.net/tutorials/simple-script/making-nano-batarangs-and-more/.
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. You can get SAMSON at https://www.samson-connect.net.





