When working with complex molecular models, one of the key challenges is filtering specific parts of a structure — like selecting only side chains, residues from a certain range, or atoms bonded to specific groups. If you’ve ever found yourself painstakingly clicking through items in your visualization software, this post might save you a lot of time.
SAMSON’s Node Specification Language (NSL) provides a precise and flexible way to select or filter structures within your molecular model. In this post, we’ll take a closer look at how you can filter nodes directly in the Document view using NSL — a method that simplifies and accelerates everyday molecular modeling tasks. This is especially helpful when you’re analyzing large assemblies or preparing subsets of atoms for further simulation or analysis.
Let’s dive into how you can use NSL expressions to filter content in the Document view.
Why filter using NSL in the Document view?
In SAMSON, you can filter nodes directly within the Document view using NSL expressions. This makes it easier to focus on meaningful parts of your molecular system — for example, visualizing only the ligands, finding specific residue ranges, or identifying atoms that meet certain spatial criteria.
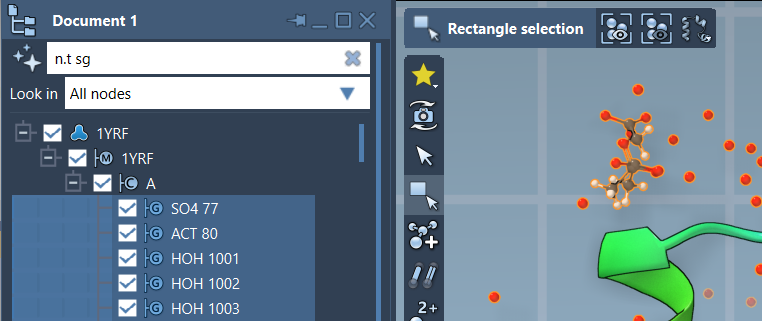
Take this NSL expression, for instance:
|
1 |
n.t sg |
This filters the Document view to show only structural groups. Once you type this in, simply press Enter to apply the filter and select matching elements.
Helpful Tip with AI Assistant
Not sure what the right NSL expression is? SAMSON offers an AI Assistant built into the interface. Just click the ![]() button next to the filter nodes field. The assistant knows your current document structure and can suggest a relevant NSL query, tailored to your selection.
button next to the filter nodes field. The assistant knows your current document structure and can suggest a relevant NSL query, tailored to your selection.
Common examples for filtering
Here are a few more practical examples you can try directly in your Document view:
n.c lig, rec— Show ligands and receptorsr.id 20:40— Show residues with IDs from 20 to 40a.c A,B— Show atoms from chains A and Bn.t bb— Show backbone nodesH in r.t ARG— Show hydrogens that are part of arginines
When these expressions are combined with other NSL operators like and, not, or within, you unlock detailed control over your selections. For example:
|
1 |
n.t r and not r.t CYS |
This matches all residues that are not cysteines.
When to use it?
Here are a few scenarios where filtering nodes in the Document view using NSL is a game-changer:
- Preparing input selections for energy calculations
- Isolating non-bonded interactions around a ligand
- Cleaning up unnecessary parts of a protein complex
By integrating NSL into your workflow through the Document view, you’ll not only interact more efficiently with structures but also reduce errors from manual selection.
To learn more about the Node Specification Language in SAMSON, you can visit the official documentation at https://documentation.samson-connect.net/users/latest/nsl/.
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. You can get SAMSON at https://www.samson-connect.net.





