Creating accurate molecular simulations often involves fine-tuning a wide variety of parameters to match the behavior and requirements of your research or design process. The Interactive Modeling Universal Force Field (IM-UFF) in SAMSON not only extends the capabilities of the traditional Universal Force Field (UFF) but also provides advanced customization options tailored for dynamic molecular modeling.
In this blog post, we’ll demystify the customization process for IM-UFF and explore how you can take full advantage of the parameters it offers to improve the accuracy and adaptability of your molecular systems.
Why Customize IM-UFF?
Whether you’re editing molecular structures, running simulations, or both, the ability to adapt a force field’s parameters is crucial. IM-UFF introduces powerful customization features that allow users to:
- Set van der Waals (vdW) interaction parameters, such as cutoff distances and switching distances for smoother energy transitions.
- Manage periodicity for neighbor list construction, ensuring optimal simulation performance.
- Automatically update molecular typization on-the-fly when atoms are added or deleted.
These features enable significant flexibility when modeling systems with topological changes, allowing the simulation to evolve as molecular structures are edited or interactively manipulated.
Key Parameters You Can Adjust
IM-UFF offers distinct modes of operation: standard UFF and IM-UFF. Here are the options typically tailored by users:
- Van der Waals cutoff: Define the vdW cutoff distance, which determines how close atoms should be before their interactions are calculated.
- Switching distance: Set the threshold for switching functions that ensure smooth transitions between atomic interactions.
- Automatic molecular typization: When IM-UFF is running with the “Static topology” option disabled, this option lets the software dynamically adjust molecular properties such as bond order and atom types in response to positional changes.
- Custom valence and coordination: In cases where topology is mutable, users can set maximum valence and coordination values to guide bond formation and structure rearrangement.
These settings help shape the molecular system’s topology while preserving realistic physics-based behavior during simulations.
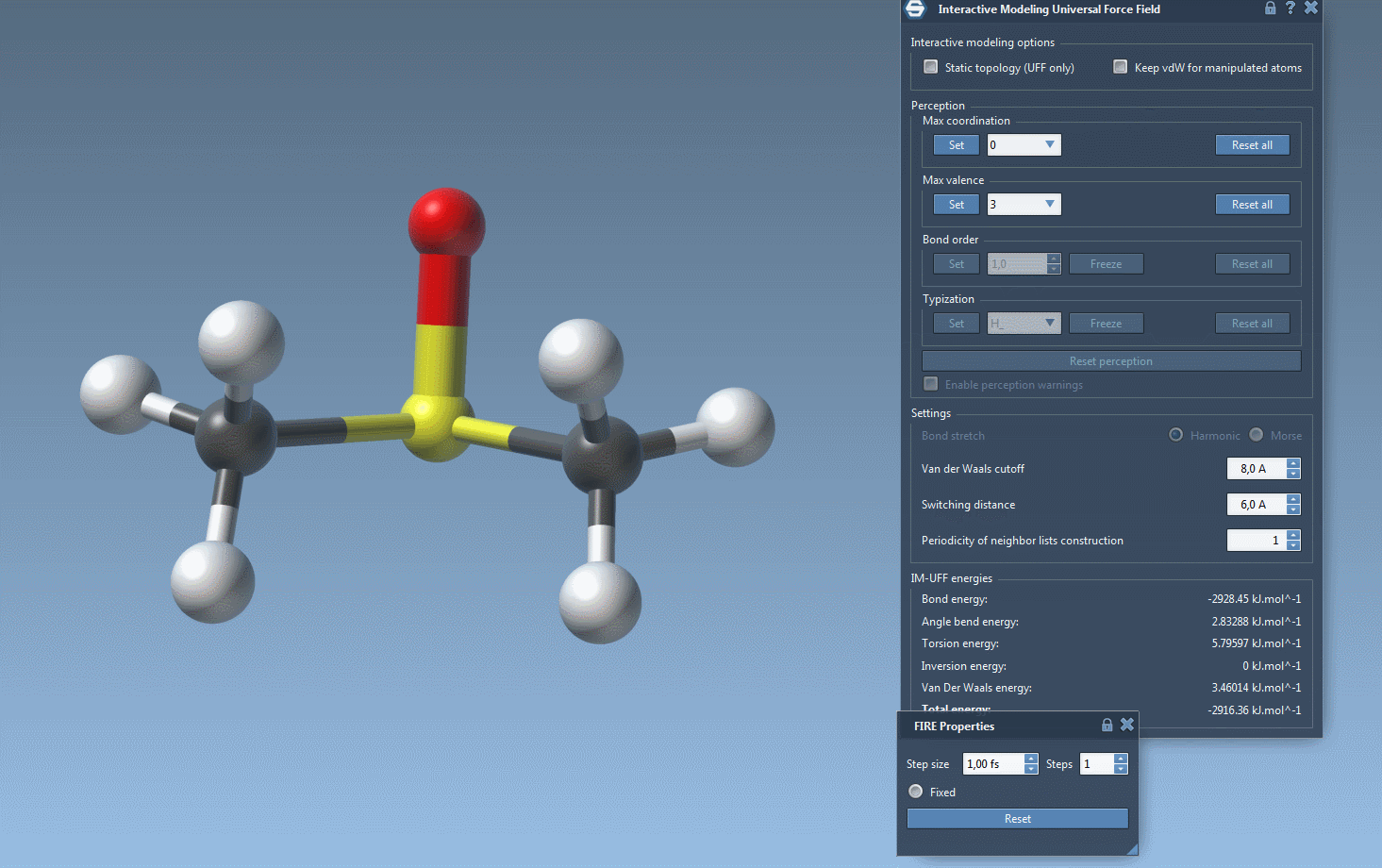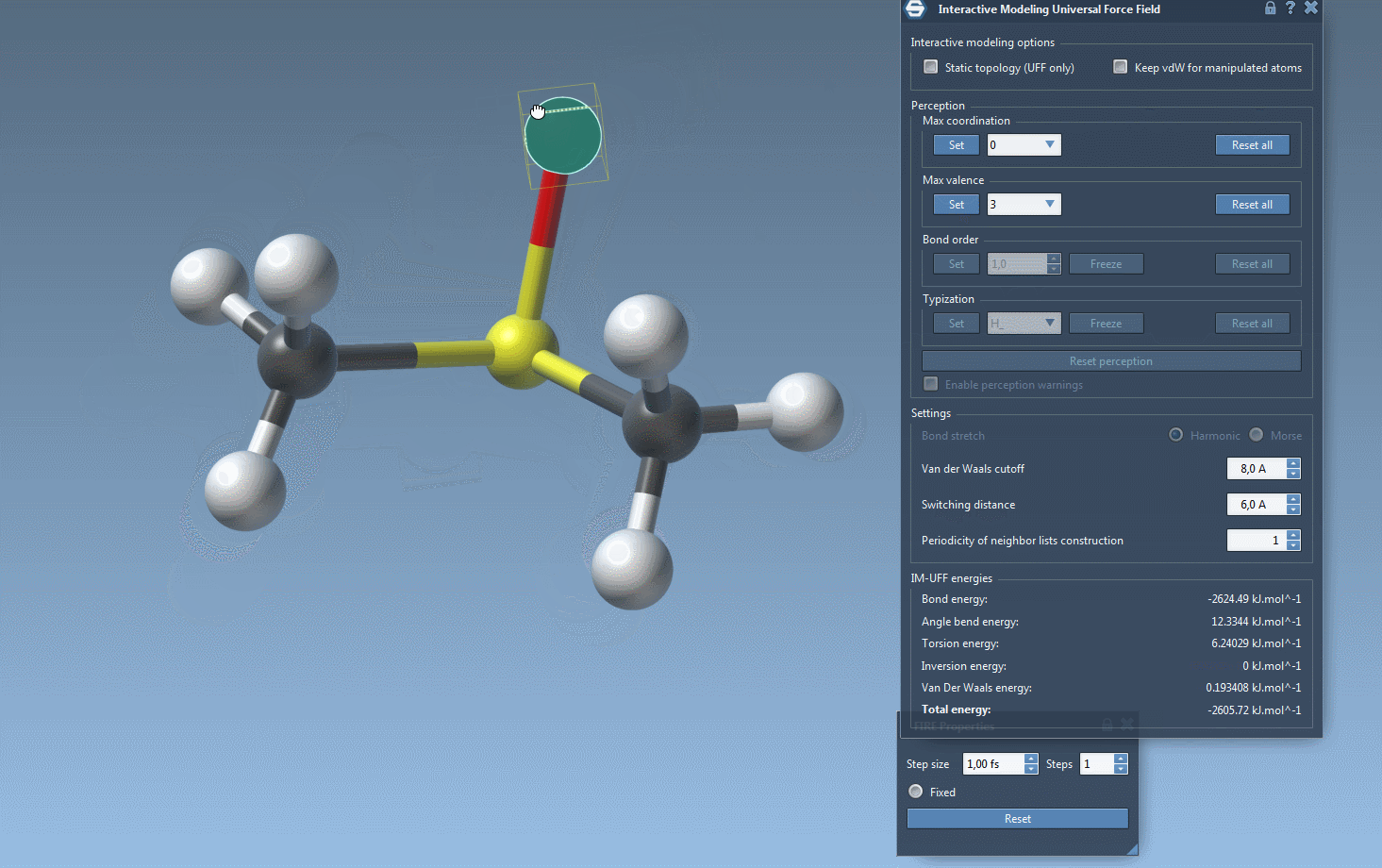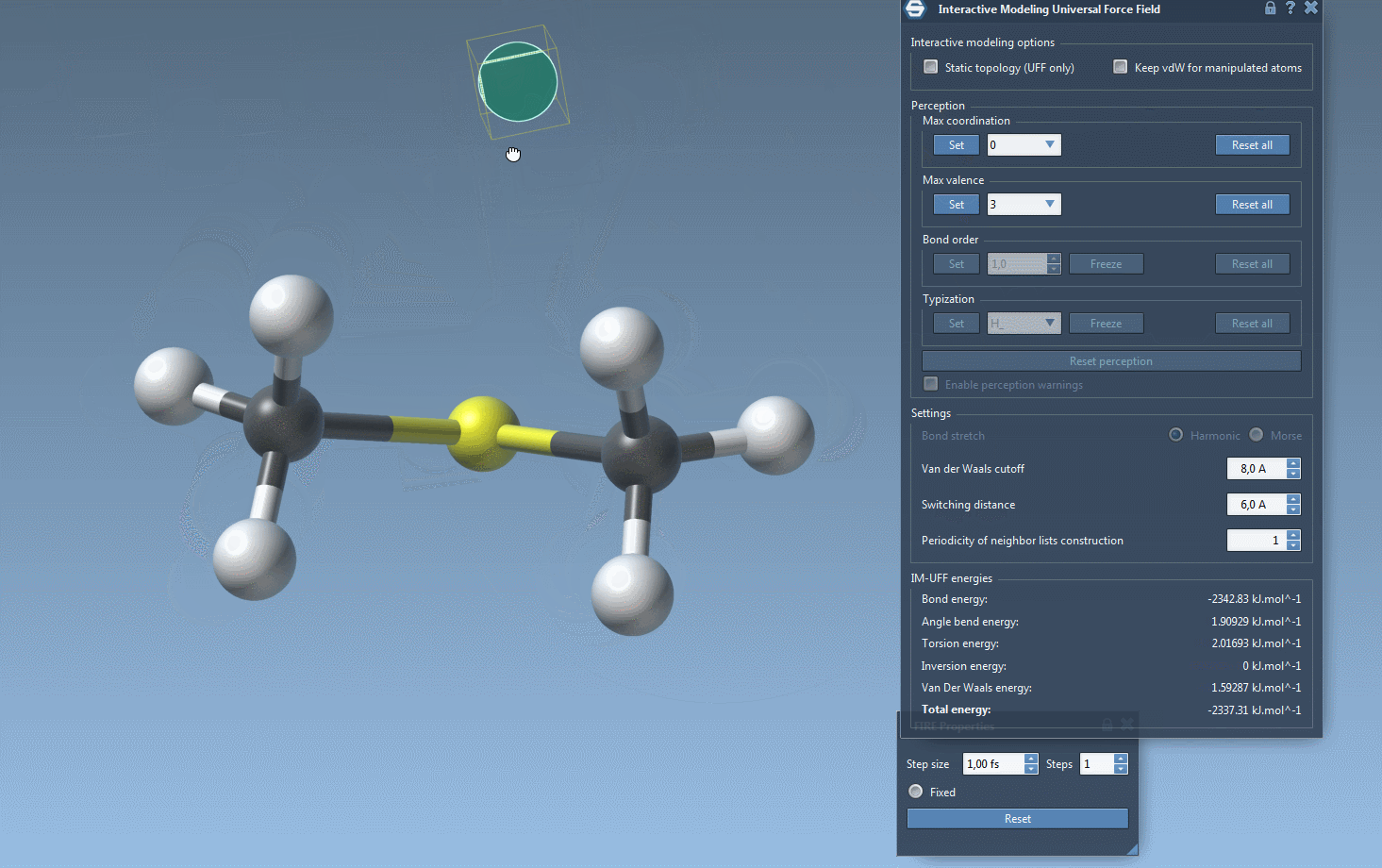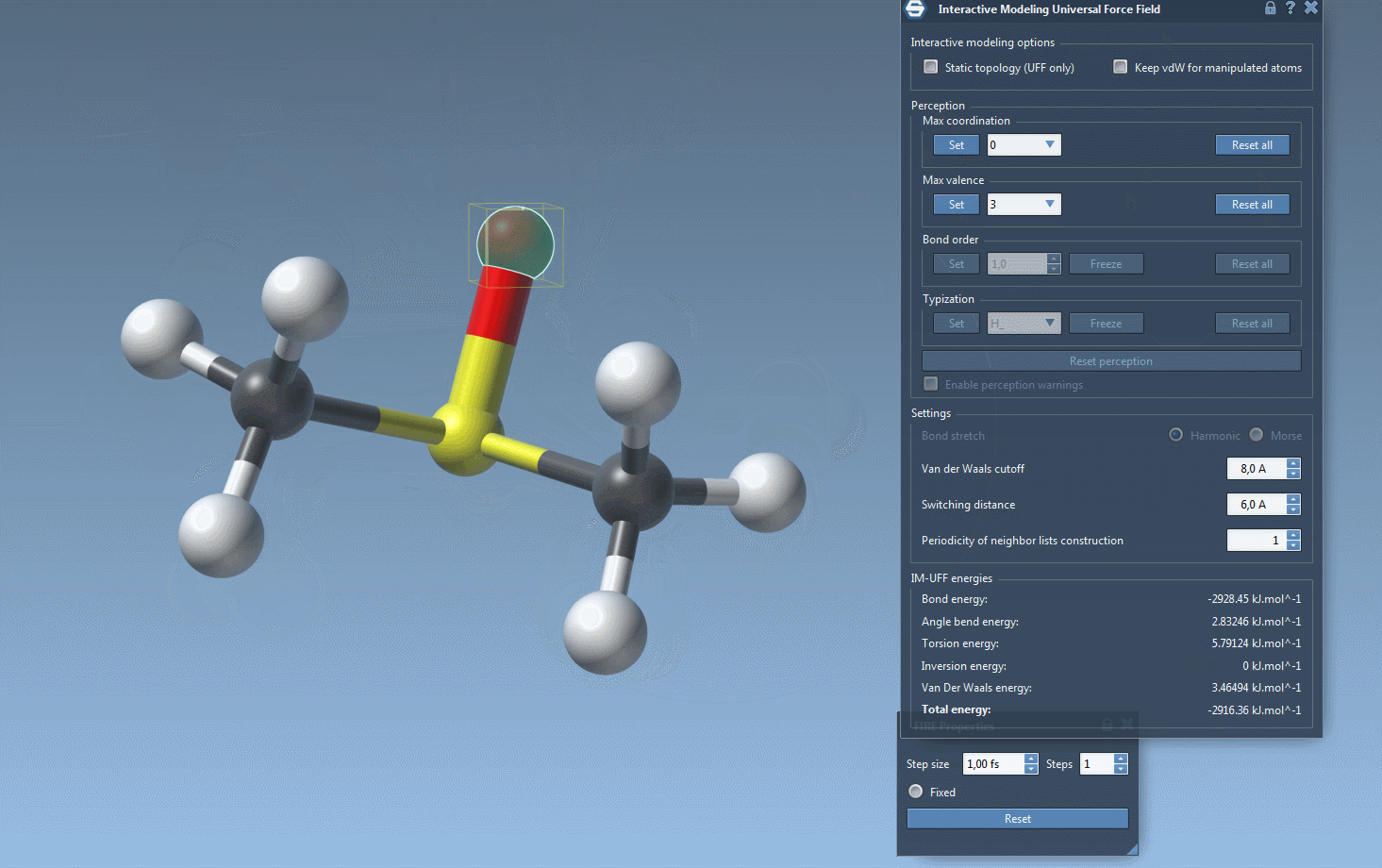
Practical Setup Tips
To implement IM-UFF with customized settings, follow these steps:
- Launch SAMSON and open your molecular document.
- Add a simulator using Edit > Simulate > Add simulator or Ctrl + Shift + M (Cmd for macOS).
- Choose the Interactive Modeling Universal Force Field interaction model.
- In the parameter window, locate sections for vdW settings and topology management.
- Adjust parameters such as cutoff distance, switching distance, and periodicity based on your simulation needs.
Additional customization options for typization or on-the-fly atom additions can further enhance your workflow. For detailed step-by-step guidelines and parameter explanations, consult the official documentation.
Conclusion
IM-UFF equips molecular modelers with tools to seamlessly blend dynamic modeling with precise configurability. Its customization capabilities make it ideal for tasks that involve frequent topological changes or detailed control of force field parameters. If you have not yet explored these features, this is a great opportunity to optimize and elevate your molecular simulations.
For additional insights and advanced configurations, we recommend visiting the IM-UFF section in the official documentation page.
Note: SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. Start building your molecular systems today by downloading SAMSON at https://www.samson-connect.net.





