Filtering and analyzing molecular structures can become time-consuming when dealing with large assemblies. For computational chemists, structural biologists, or anyone routinely working with complex molecular data, pinpointing specific residues, bonds, chains, or functional groups quickly is essential—but often tedious.
Fortunately, SAMSON offers a flexible and powerful way to filter nodes interactively using NSL: the Node Specification Language. One of its most practical applications is in the Document View, where you can type NSL expressions to focus on the precise elements of your molecular model you’re interested in.
Filtering in Document View
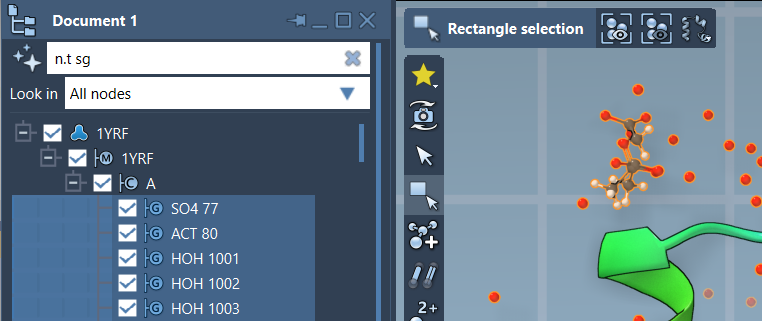
Inside the Document View, an entry box allows you to type NSL expressions. As you type, the interface provides real-time filtering, and pressing Enter will select the matching nodes. For example, entering:
|
1 |
n.t sg |
…will match all structural groups in the document (this is the short version of node.type structuralGroup).
You can also use NSL to filter more specific elements such as particular residue types, selections based on atomic symbols, distances, or logical combinations.
Here are a few useful examples you can try right away in the Document View:
r.t ALA— matches all alanine residuesa.el H— matches all hydrogen atomsr.id 10:20— matches residues with IDs between 10 and 20C or H— matches carbon or hydrogen atomsn.t r and not r.t GLY— matches residues that are not glycines
Interactive Assistance with AI
Don’t feel like memorizing syntax? You can click the Ask AI button ![]() next to the filter entry field in the Document View. The AI Assistant analyzes the active document and helps craft the appropriate NSL expression for your context—particularly useful when working with unfamiliar molecules or new naming conventions.
next to the filter entry field in the Document View. The AI Assistant analyzes the active document and helps craft the appropriate NSL expression for your context—particularly useful when working with unfamiliar molecules or new naming conventions.
Combining Filters
The real power emerges when combining expressions logically. For example:
|
1 |
r.t LYS and a.el N |
…matches nitrogen atoms that belong to lysine residues.
Or use proximity filters like:
|
1 |
n.t r within 5A of "GLY 15" |
…to get all residues within 5 angstroms of GLY 15.
Visual Feedback
The results of your filters are immediately reflected in the interface, helping you verify selections on-the-fly. This speeds up model preparation, comparison, or exporting parts of your macromolecules for further analysis.
Discovering how powerful NSL becomes in Document View can save hours of manual clicking and searching. It’s one of those small workflow upgrades that makes a big difference over time.
To learn more about NSL and explore more advanced features, visit the NSL documentation page.
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. Get SAMSON at https://www.samson-connect.net.





