In molecular modeling, selecting the right atoms can be crucial. Whether you’re preparing a simulation system, modifying a structure, or simply visualizing specific regions, being able to define custom selection rules can save both time and effort.
If you’ve ever been frustrated by limited or rigid selection tools in modeling environments, you’re not alone. Many molecular modeling platforms offer only basic ways to select atoms (like selecting by residue name or element type). But what if you want to select atoms based on coordinates, visibility, or belonging to specific parts of a structure — such as an amino acid backbone or a defined region in 3D space?
This is where SAMSON’s Atoms Selector Extension becomes especially useful. It enables users to craft highly specific selections using mathematical expressions that are both powerful and readable.
How It Works
The Atoms Selector Extension uses a scripting syntax based on the same variables and logical constructs as the Simple Script extension but is focused only on selecting atoms. With this tool, you can write expressions like:
|
1 |
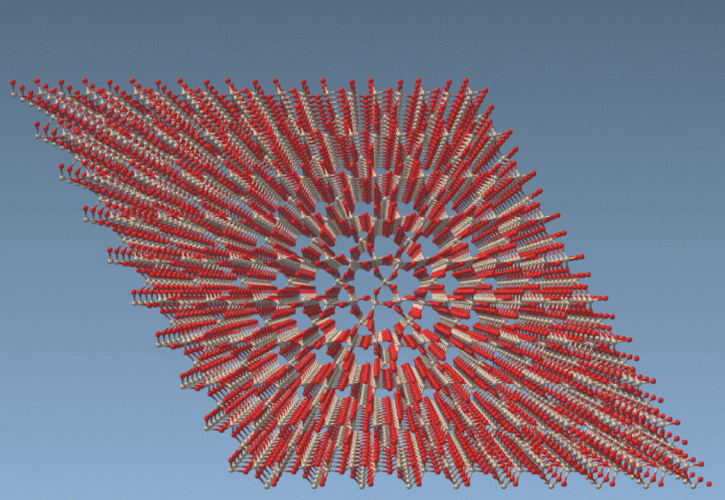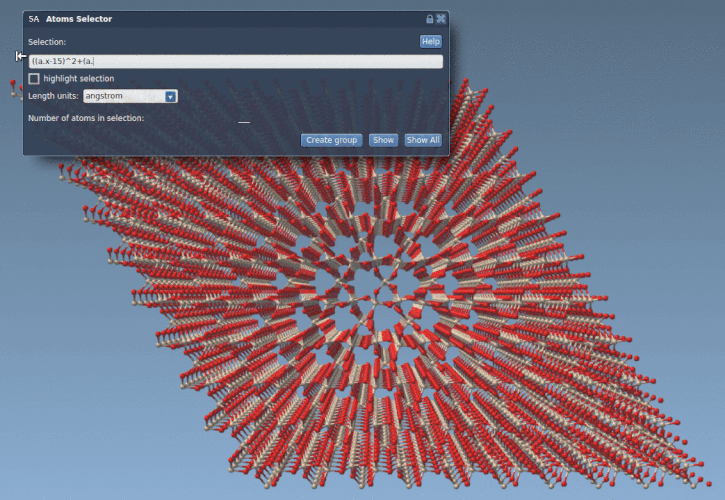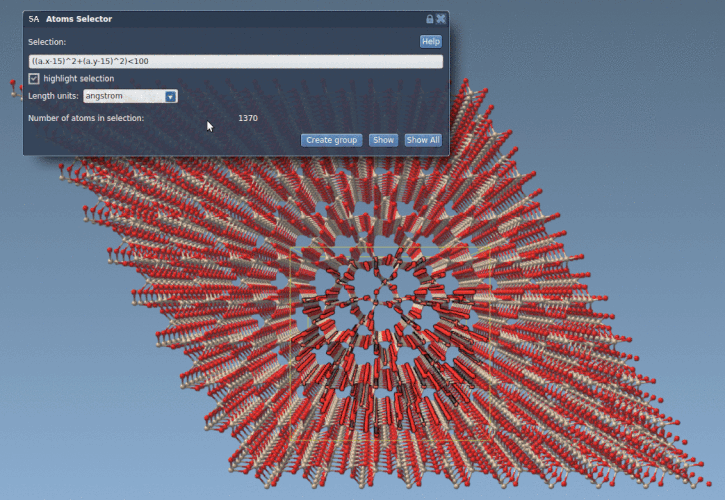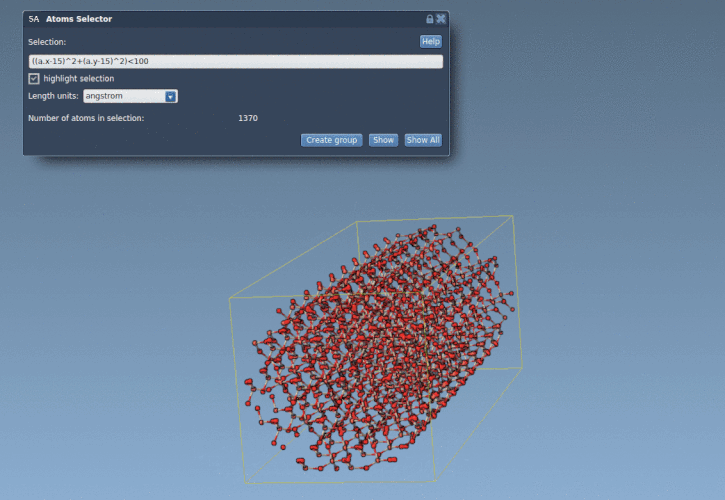
((a.x-15)^2 + (a.y-15)^2) < 100 |
This selects all atoms within 10 Å of the point (15, 15) in the xy-plane — essentially cutting a cylinder of atoms from a structure such as a quartz crystal.
The Variables You Can Use
The selectors support a wide range of atomic attributes. For example:
a.x,a.y,a.z: coordinatesa.element,a.symbol: element names or symbolsa.visibilityFlag,a.water,a.aminoAcidBackbone: logical flags about the atom’s propertiesa.chainID,a.residueSequenceNumber: structural identifiers
This means you can do things like:
|
1 |
a.aminoAcidBackbone == true and a.z > 5 |
…to select atoms that are part of an amino-acid backbone and are positioned above a defined z-coordinate.
Why It’s Worth Using
With these expressions, structure curation becomes faster, cleaner, and more accurate. You can:
- Isolate atoms in geometric regions like spheres or boxes
- Target atoms based on chemical or physical properties
- Automate selection for repetitive workflows
Compared to clicking or navigating menus, this method scales dramatically better with system size — especially useful for crystals, complex biomolecules, or nanostructures.
Here’s a quick example to select all atoms with x and y coordinates greater than 0:
|
1 |
a.x > 0 and a.y > 0 |
Or to select all carbon atoms in a system:
|
1 |
a.element == 'Carbon' |
Getting Started
To try this out, install the Atoms Selector Extension through SAMSON and access it from the Extension menu.
You can explore more examples and available variables on the official documentation.
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. You can download SAMSON at https://www.samson-connect.net.





