Building biologically relevant molecular systems often involves embedding a protein within a lipid bilayer or surrounding it with a lipid monolayer. For molecular modelers, manually placing lipids around complex protein structures can be time-consuming and error-prone. Ensuring correct orientation, packing lipids without overlaps, and generating realistic systems can require scripting or external tools. Fortunately, this task becomes much simpler with the Molecular Box Builder extension in SAMSON.
This post walks you through a useful workflow: wrapping a transmembrane or membrane-adjacent protein with a lipid layer using Molecular Box Builder. By the end, you’ll have a reproducible way to create realistic protein-lipid assemblies for further simulations or analysis.
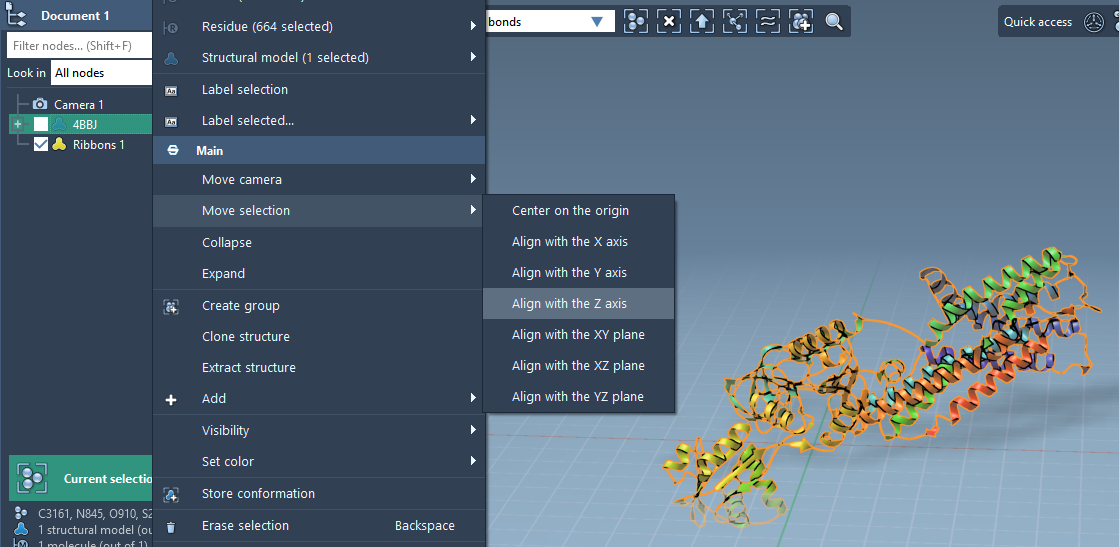
Step 1 – Align Your Protein
To build around a membrane-bound protein, start by orienting it properly:
- Load your protein (e.g., PDB structure 4BBJ).
- Right-click it in the Document view.
- Select Move selection > Align with Z axis.
- Then choose Move selection > Center on the origin.
Step 2 – Set the Lipid Molecule
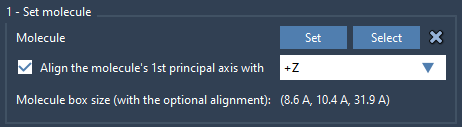
Next, import the lipid you wish to use (e.g., a phospholipid like POPC):
- Import a lipid topology or structure into your SAMSON document.
- Select the molecule, click Set in the Molecular Box Builder app.
- Use the orientation setting to align the lipid along the
+Z-axis.
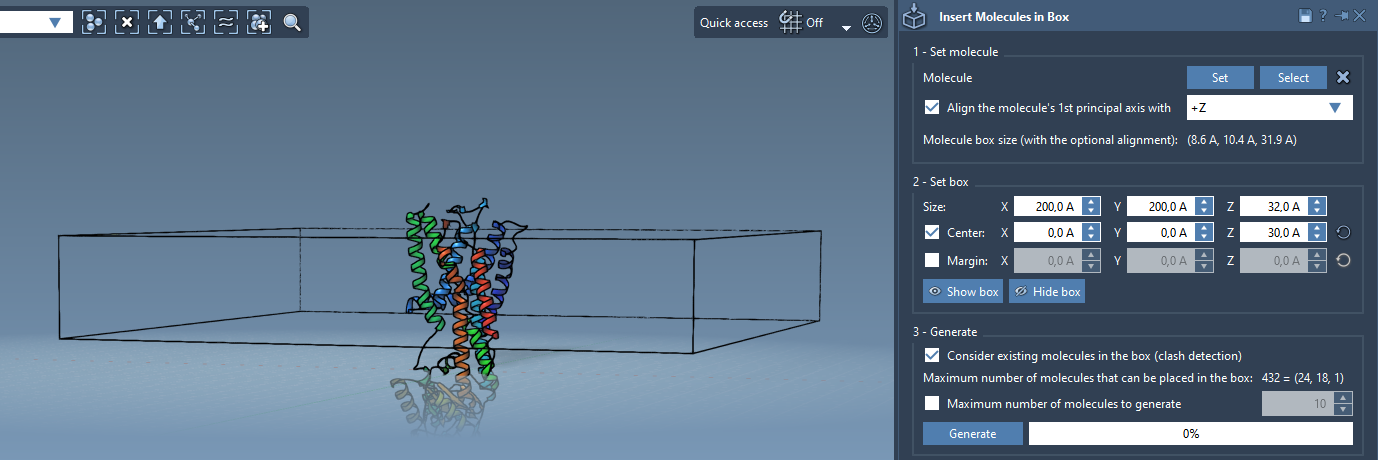
Step 3 – Define the Box
The lipid layer will be added in a box that surrounds the protein:
- Check Center and set the box to be centered around your protein.
- Adjust the height in
Zto accommodate a monolayer or bilayer depending on the desired result. - Adjust margins between lipids if necessary to improve packing efficiency.
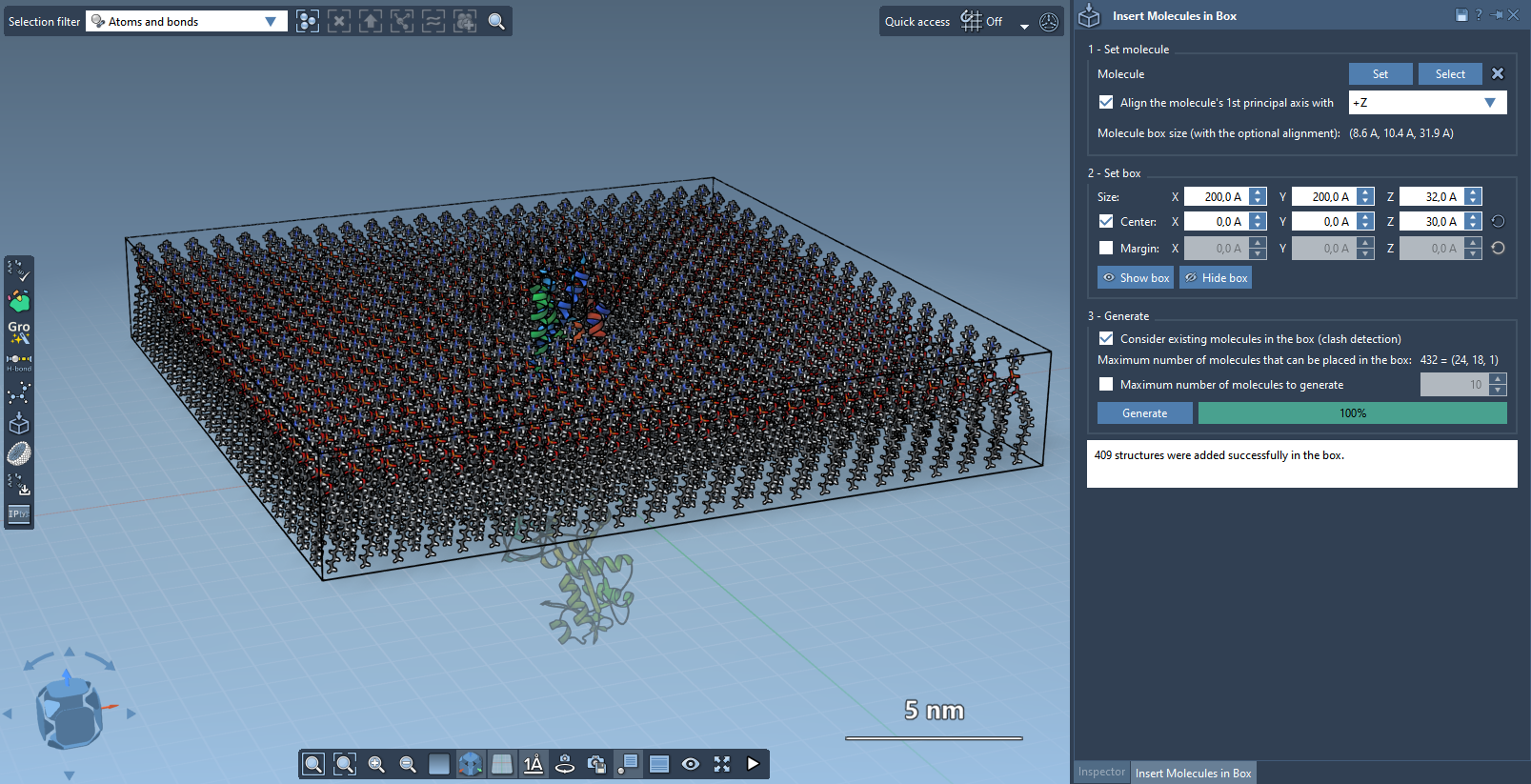
Step 4 – Generate the Lipid Layer
Before generating, make sure you enable Consider existing molecules in the box to avoid inserting lipids inside the protein volume.
- Enable the collision check.
- Click Generate.
Voilà — your protein is now wrapped with a lipid layer:
What About Lipid Bilayers?
You can go a step further and assemble a bilayer by generating two layers sequentially:
- First generate the
+Zlayer with the lipid aligned accordingly. - Then shift the box slightly along
Z. - Set the lipid’s alignment to
-Zand generate again to form the second layer.
This mechanic gives you flexibility for studying asymmetric membranes, emulating more realistic biological systems.
Where to Go From Here?
Once your membrane-protein system is built, you can proceed with energy minimization, solvation, and equilibration using tools such as the GROMACS Wizard.
To learn more about using the Molecular Box Builder for different kinds of systems—from solvent boxes to nanostructure design—visit the original documentation page here.
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. You can get SAMSON at https://www.samson-connect.net.





