When modeling complex molecular systems, selecting the right atoms is often a necessary but tedious task. Visual selection can be uncomfortable in dense structures, and name-based selection isn’t always flexible enough. But with mathematical expression-based selection, you can gain precision and save time, especially in periodic structures or large atomic assemblies.
The Atoms Selector Extension in SAMSON offers an intuitive way to select atoms programmatically with concise mathematical queries. This post explores how to use it to control exactly which atoms appear in your design space—and why this can matter to a molecular modeler.
Why this helps
If you’re working with large systems (like crystals, biomolecules, or nanostructures), you might want to:
- Isolate atoms within a particular region of space (e.g. spherical, cylindrical, or slab-shaped regions)
- Select atoms based on properties, such as atomic number, partial charge, position, or visibility
- Combine multiple selection criteria
- Avoid manual, error-prone visual selection
How it works
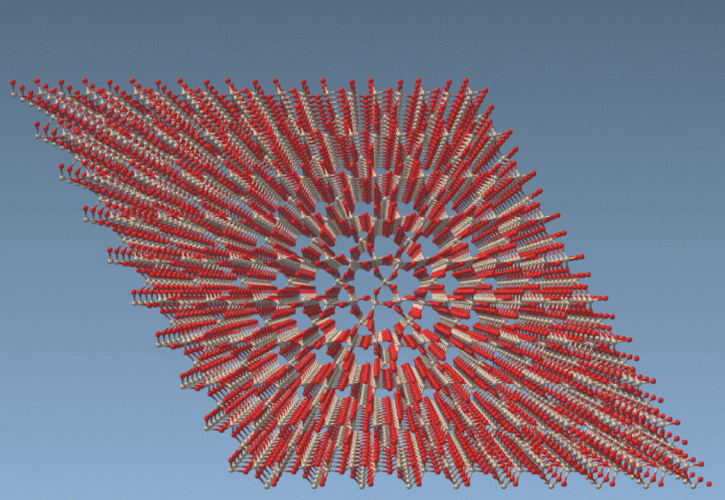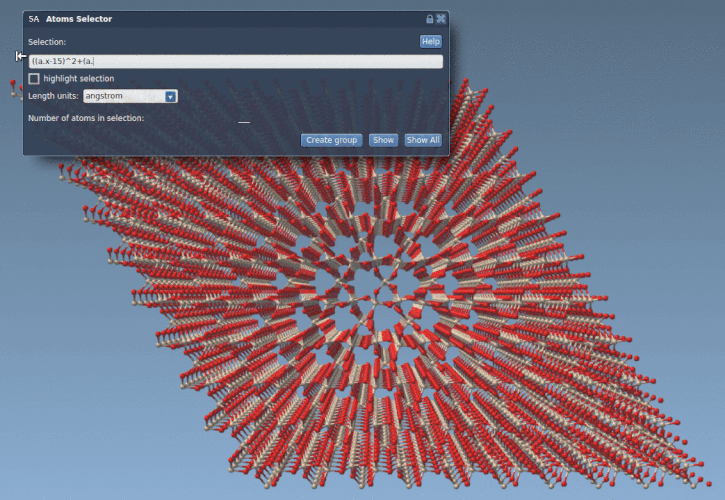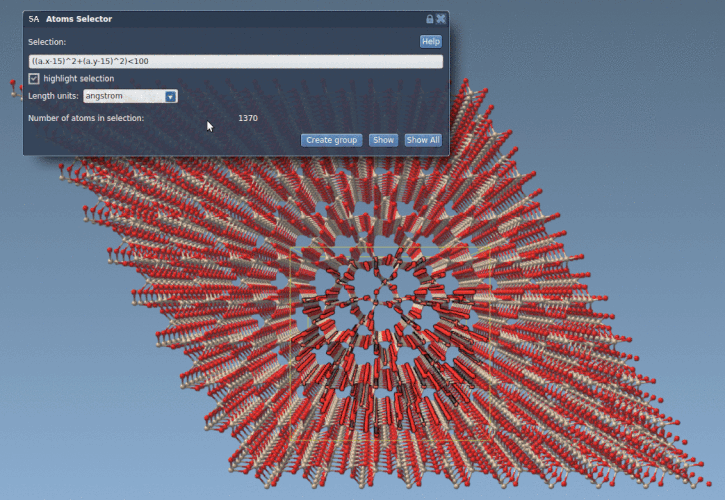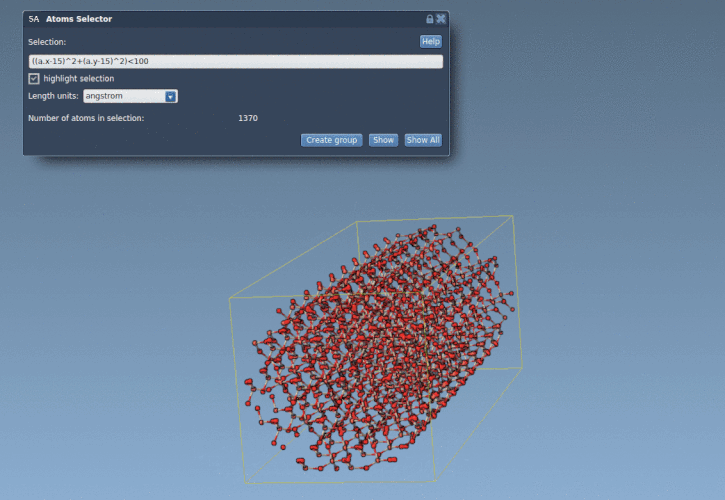
The Atoms Selector Extension uses the same variables, operators, and functions as the Simple Script Extension. You only need to provide a boolean expression. For example, the following line will select all atoms within 10 Å of the point (15, 15):
|
1 |
((a.x-15)^2 + (a.y-15)^2) < 100 |
This is especially helpful for cutting out specific shapes from a crystal or material. Consider this quartz fragment, where we’ve isolated a cylindrical region based on atomic coordinates:
You can use all standard mathematical and logical functions—such as abs(), sqrt(), >, and, and more—to define the region or characteristics of atoms you want to select. Here’s another example:
|
1 |
(a.e == 'Carbon') and (a.z > 5) |
This expression selects only carbon atoms above a height threshold.
Even faster: Use the keyword all
Need to quickly select everything in the model? Just write:
|
1 |
all |
This is especially useful to reset selections or prepare a model before running another operation.
Useful tips
- Variable and function names are case-insensitive.
- Quotation marks (
' ') are used for element names:'Oxygen','Fe', etc. - You can combine multiple properties using logical operators:
and,or,not.
Why this matters
This type of fine-grained selection lets researchers and students focus more on design and analysis, and less on the mechanics of preparing the model. It becomes faster to perform operations like isolating functional groups, applying transformations, or creating nano-patterns.
To try it for yourself, head to the Atoms Selector Extension in SAMSON. You’ll find a flexible and robust way to manage large atomic systems—without the hassle of manual selection or scripting overhead.
To learn more, visit the full documentation page: https://documentation.samson-connect.net/tutorials/simple-script/making-nano-batarangs-and-more/
SAMSON and all SAMSON Extensions are free for non-commercial use. You can download SAMSON at https://www.samson-connect.net





