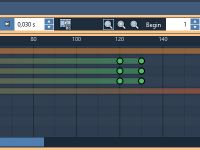
Bringing Molecules to Life: An Introduction to SAMSON’s Animator
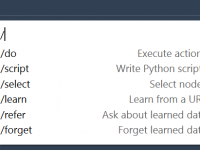
Tired of Clicking Around? Interact with Your Molecular Model Using Plain English
How to Select Atoms with Mathematical Precision in SAMSON
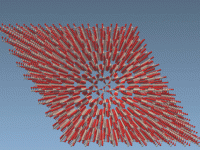
Building Carbon Nanotubes with SAMSON’s Pattern Editors
A common challenge in molecular modeling—especially in nanotechnology and materials science—is constructing large, periodic structures like carbon nanotubes (CNTs). These structures are often composed of repeated rings or motifs, and manually placing each unit is time-consuming and error-prone. If you’ve…
Avoid Misassignments: A Simple Way to Set Up Protein-Ligand Systems for NMR2
Less Clicking, More Clarity: Save Time with Customized Visual Presets in SAMSON
Following the Molecule: Using Camera Animations to Create Molecular Tours
Make Your Camera Follow Molecular Motion Automatically
Choosing the Right Palette: Discrete Color Palettes in Molecular Modeling
When working with complex molecular systems, clarity is essential. Whether you’re highlighting different protein chains, annotating functional domains, or distinguishing between ligands and cofactors, visual differentiation helps you and others understand your molecular model more effectively. This is where discrete…